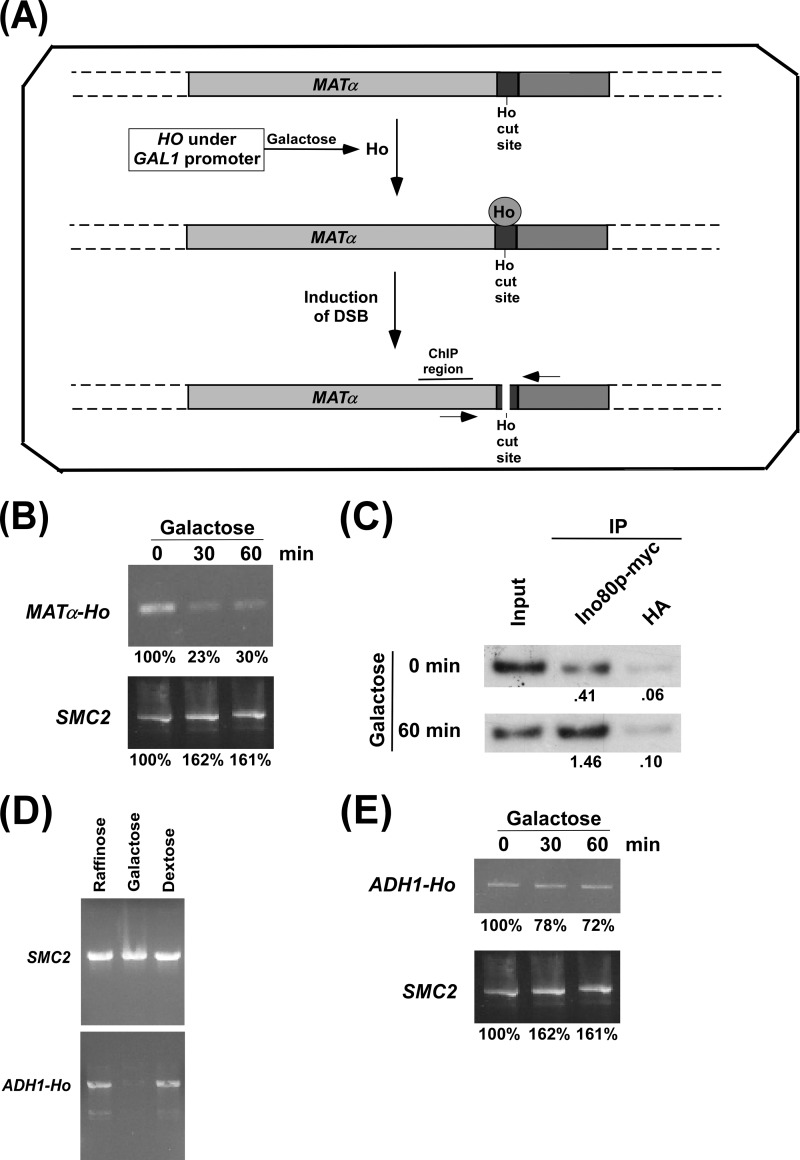
FIGURE 2.
Analysis of DSB at the MATα and ADH1 loci. A, schematic diagram showing the generation of DSB at the MATα locus following the induction of HO expression. The primers flanking the Ho cut site are marked by two arrow-headed lines and were used in PCR for analysis of DSB. B, PCR analysis of DSB at the MATα locus. The yeast strain that contains a Ho cut site at the MATα locus and expresses HO under the GAL1 promoter was initially grown in YPR up to an A600 of 0.9 (log phase) and then switched to YPG for 30 and 60 min (an A600 of 1.0 is ∼3 × 107 yeast cells/ml; 46). Genomic DNA was analyzed by PCR to determine DSB using the primer pair flanking the DSB site. The PCR signal at 0 min was set to 100. The PCR signals at 30 or 60 min in YPG were normalized with respect to the 0 min time point in YPG. C, the ChIP assay for analyzing the recruitment of Ino80p to the DSB site. The yeast strain (ASY32) was grown as in B prior to cross-linking. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using an anti-myc antibody (9E10, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) against myc-tagged Ino80p. An anti-HA was used as a nonspecific antibody control. The ratio of immunoprecipitate over the input in the autoradiogram is indicated below the immunoprecipitated band. D, analysis of DSB at ADH1 in YPR, YPG, and YPD media. The yeast strain PCY23 was grown in YPR, YPG, or YPD up to an A600 of 0.2 at 30 °C and harvested. Genomic DNA was analyzed for DSB by PCR using the primer pair flanking the HO cut site at ADH1. E, induction of DSB at the ADH1 locus. The yeast strain PCY23 was grown as in B.