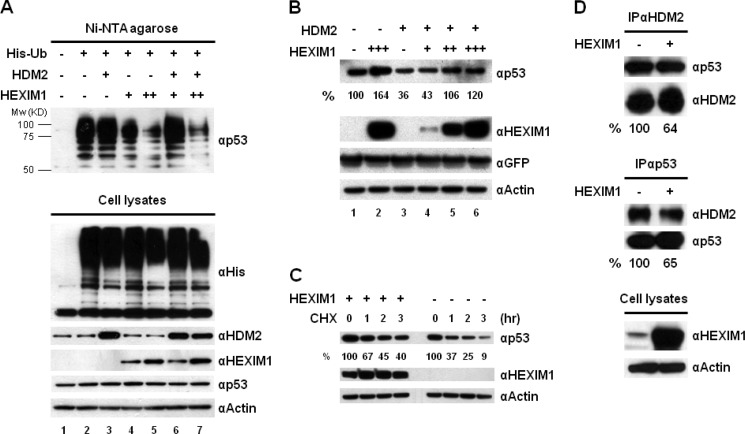
FIGURE 4.
Overexpression of HEXIM1 inhibits p53 ubiquitination and disrupts the interaction between p53 and HDM2. A, MCF7 cells were co-transfected with the His-Ub, HDM2, and HEXIM1 expression vectors as indicated. To prevent the degradation of ubiquitinated p53, MG132 was added into the culture before harvesting. The cell lysates prepared from the transfected cells were incubated with Ni-NTA-agarose to capture His-Ub-conjugated proteins. Elutions from the Ni resin were analyzed by Western blot using an anti-p53 antibody. The expression of His-Ub, HDM2, HEXIM1, p53, and actin was examined. B, MCF7 cells were transfected with HDM2, HEXIM1, and GFP expression vectors in the indicated combinations. The GFP plasmid was included in all transfections to normalize the transfection efficiency. The quantitation of p53 protein is presented in percentage after normalizing with GFP proteins. C, MCF7 cells were transfected with an empty vector or a HEXIM1 expression plasmid. Mock- and HEXIM1-transfected cells were incubated with 100 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for 0, 1, 2, and 3 h. The quantitation of p53 is presented in percentage after normalizing with actin. D, cell lysates of the mock- and HEXIM1-transfected MCF7 cells were used to analyze the association between p53 and HDM2 by IPs. MG132 was included in the culture before harvesting. The amounts of p53 and HDM2 proteins immunoprecipitated by an anti-HDM2 antibody were quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The HDM2 protein precipitated in the IP against HDM2 was used as the input to normalize the amount of p53 protein detected in the IP. Reverse IP using an anti-p53 antibody was carried out and the same quantitative methods were utilized to examine the changes of p53-HDM2 interaction caused by HEXIM1 overexpression. The experiments were performed at least twice and similar results were obtained.