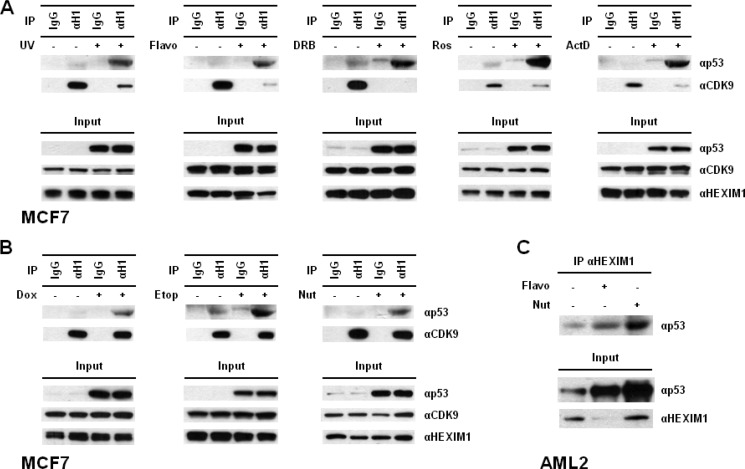
FIGURE 5.
Functional connection between p53 induction and p53-HEXIM1 interaction. A, MCF7 cells were treated with UV, flavopiridol (i.e. Flavo, 1 μm), DRB (100 μm), roscovitine (i.e. Ros, 20 μm), or actinomycin D (i.e. ActD, 30 nm). The DMSO-treated cells were used as controls since all compounds were dissolved in DMSO. The HEXIM1-p53 and HEXIM1-CDK9 associations were determined by IP using an anti-HEXIM1 antibody (i.e. αH1), followed by Western analysis. The normal IgG was used as the control for IP experiments. The protein levels of p53, HEXIM1, and CDK9 in cells were also examined. B, after incubated with doxorubicin (i.e. Dox, 1 μm), etoposide (i.e. Etop, 10 μm), or nutlin-3 (i.e. Nut, 10 μm), the cell lysates prepared from the treated MCF7 cells were analyzed by IP, followed by Western blotting. C, AML2 cells were incubated with flavopiridol (i.e. Flavo, 1 μm) or nutlin-3 (i.e. Nut, 30 μm) and the interaction between p53 and HEXIM1 was analyzed by IP. The protein levels of p53 and HEXIM1 in the cell lysates were also examined. Flavo, DRB, and Ros are CDK-inhibiting compounds; ActD, transcription inhibiting compound; Dox and Etop, DNA damage compounds; Nut, HDM2 antagonist.