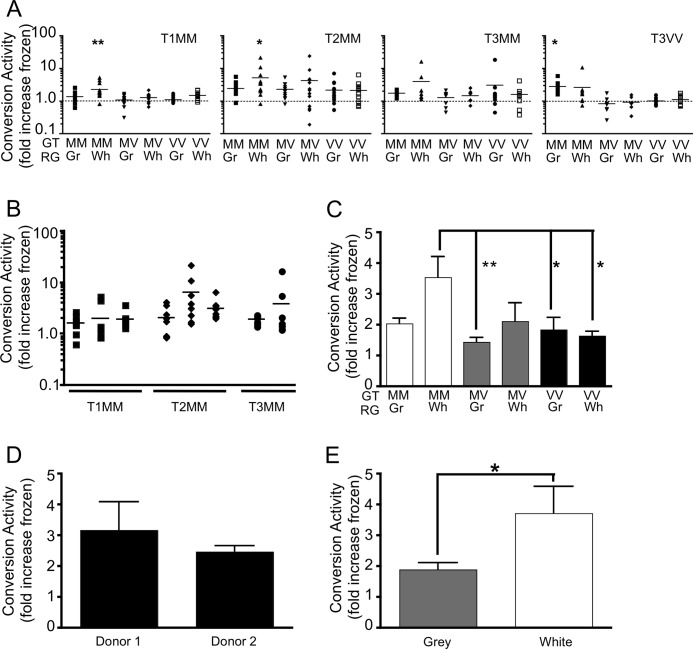
FIGURE 3.
Sporadic CJD PrPSc has PrP genotype and brain region-specific requirements for in vitro conversion activity. A, protease-pretreated sporadic CJD PrPSc (T1MM, T2MM, T3MM, and T3VV) used to generate PrPres from a PrPC substrate enriched for the gray (Gr) or white (Wh) matter regions (RG) of brain tissue with a PrP codon 129 genotype (GT) either MM, MV, or VV. Conversion activity is the -fold increase in PrPres for each incubated sample over its corresponding control frozen sample. The dotted line indicates no conversion activity. Significance (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01) was calculated relative to the mean conversion activity detected in the presence of a mouse brain homogenate using one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett's Multiple Comparison Test. B, conversion activity of individual sources of T1MM (n = 3), T2MM (n = 3), and T3MM (n = 2) sporadic CJD PrPSc using PrPC substrate from gray and white matter of the methionine homozygous donors. C, ability of PrPC substrates with different codon 129 genotypes and derived from different brain regions to support PrPres formation by any sporadic CJD subtype. D, ability of methionine homozygous PrPC substrates derived from the gray and white matter of two different donors, to support the conversion activity of T1MM and T2MM PrPSc. E, conversion activity of gray and white matter-enriched methionine homozygous substrates seeded with T1MM and T2MM sporadic CJD PrPSc. Error bars, S.E.