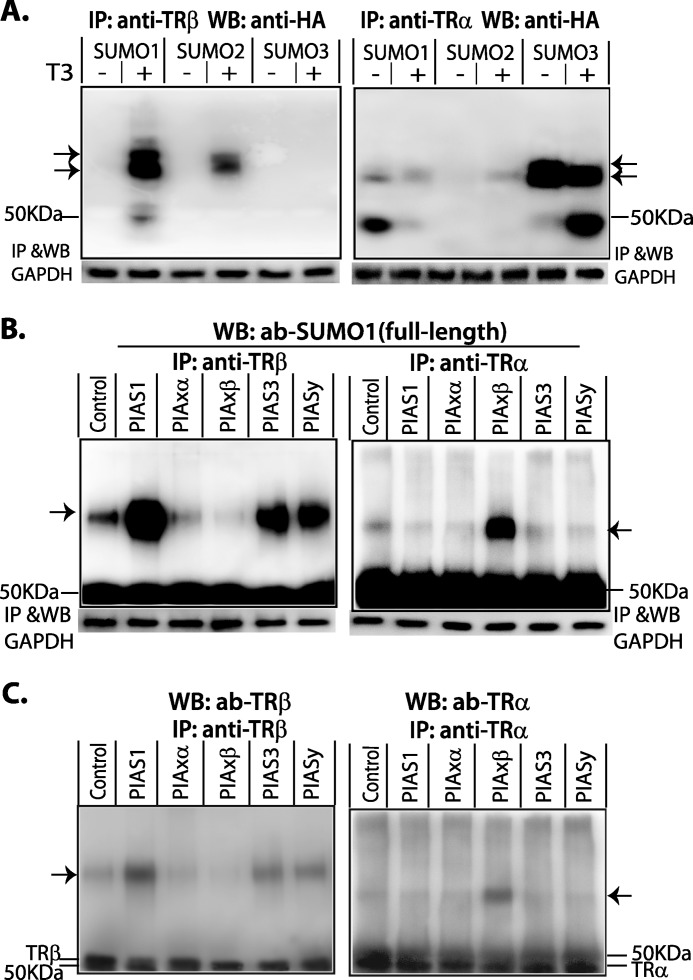
FIGURE 2.
Sumoylation of TR isoforms. A, ligand effects and ligase preference for sumoylation HepG2 cells were transfected with human SUMO (SUMO1, 2, or 3)-HA, and human TRα or human TRβ expression vectors and grown in serum-free medium for 16 h prior to treatment with or without T3 (50 nm) for 4 h. Cell lysate was used for IP with anti-TRα or anti-TRβ antibodies (ab). Immunoprecipitated protein complexes were subject to 7.5% SDS-PAGE. For detection of TR-SUMO conjugation in WB, anti-HA was used to detect SUMO(1, 2, or 3)-HA. B, E3 ligase requirement. HepG2 cells were transfected with PIAS family members. Control cells were not transfected with E3 ligase. Cells, including control cells, were treated with T3 (50 nm) for 4 h for the detection of TRβ-SUMO conjugation, but without T3 for detection of TRα-SUMO. Anti-TRα or anti-TRβ antibodies were used in IP and anti-SUMO1 (full-length) in WB. After IP with anti-TRs, the cell lysates were then used for IP with anti-GAPDH and WB GAPDH, which was used as a protein input control. C, verification of TR in SUMO-conjugated bands in B. The membrane in B was stripped, checked with chemiluminescent exposure to confirm the absence of residual activity, and then incubated with anti-TR antibodies as shown. Arrows show SUMO-TR complexes.