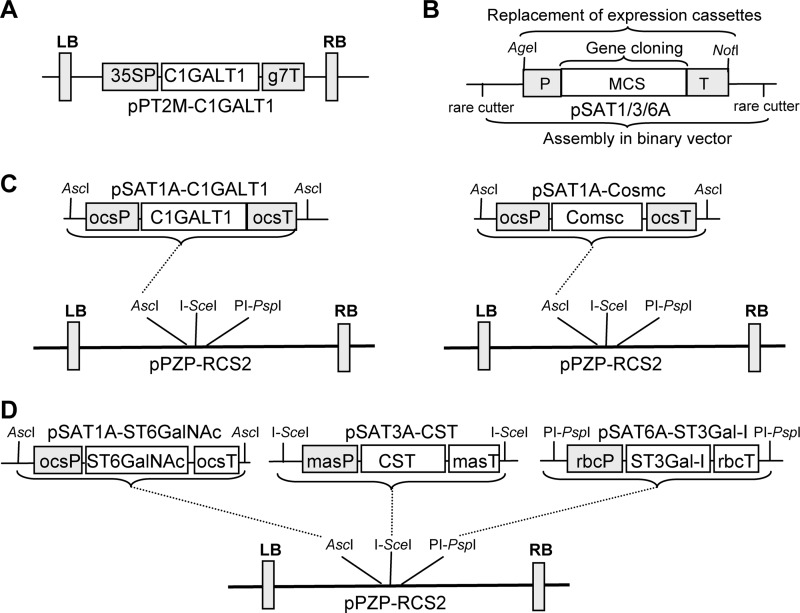
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of newly generated vectors. A, binary vector for the expression of the Drosophila C1GALT1 is shown. B, shown are structural features of the pSAT series of auxiliary vectors (pSAT1A, pSAT3A, and pSAT6A) for the assembly of promoter-gene-terminator cassettes. Rare-cutting enzymes flanking each pSAT vector are used to transfer the expression cassettes into the expression vector pPZP-RCS2. C, shown is the outline of the cloning strategy for expression of human C1GALT1 and its chaperone COSMC. D, shown is a schematic representation of the cloning strategy for the multiple gene expression vector. The CST, ST3Gal-I, and ST6GALNAc-III/IV open reading frames were cloned into different pSAT auxiliary vectors and were then sequentially assembled in pPZP-RCS2 using specific rare-cutting enzymes. In the final constructs all three proteins are expressed under different promoter and terminator sequences. 35SP, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; g7T, Agrobacterium gene 7 terminator; ocsP, octopine synthase promoter; ocsT, octopine synthase terminator; rbcP, rubisco small subunit promoter; rbcT, rubisco small subunit terminator; masP, manopine synthase promoter; masT, manopine synthase terminator; LB, left border sequence; RB, right border sequence.