Figure 4. CRF-induced responses in NPS-EGFP neurons.
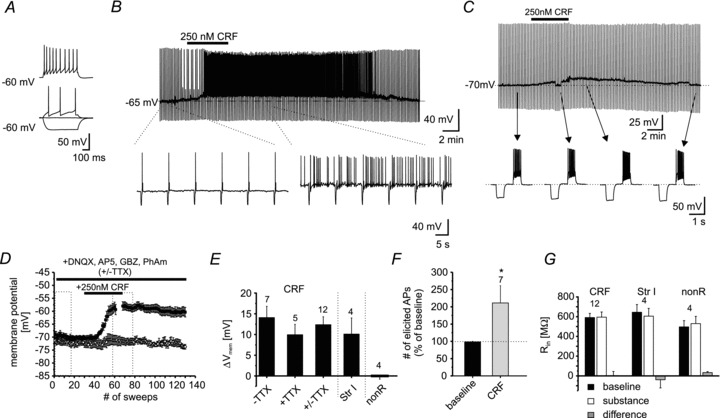
A, example recording of an individual NPS-EGFP neuron in current-clamp mode at a membrane potential of −60 mV. Hyper- and depolarizing currents (depicted are injections of −50, 0, +20 and +70 pA) were injected to analyse passive and active membrane properties. B, example recording of a single NPS-EGFP neuron at a membrane potential of −65 mV. In the presence of 250 nm CRF the neuron depolarized and generated spontaneous action potentials. C, example trace of an NPS-EGFP neuron recorded in current-clamp mode at a membrane potential of −70 mV. The bar indicates the application of 250 nm CRF for 5 min. Hyperpolarizing current injections (−60 pA; 500 ms duration) were done to control the input resistance. Depolarizing currents (+70 pA; 500 ms duration) were injected to elicit action potentials. Magnified examples are shown from the recording at time-points indicated by the arrows. During the CRF-induced depolarization, the membrane potential was re-adjusted to −70 mV to minimize the effects of voltage-dependent conductances on the input resistance. D, time course of the CRF-induced depolarization in NPS-EGFP neurons. Dashed boxes indicate the time intervals taken for quantification. E, quantification of the CRF-induced shift of the membrane potential (−TTX, recording in absence of TTX; +TTX, recording in presence of TTX; +/−TTX, pooled data; Str I, application of 250 nm Stressin I; nonR, non-responsive NPS-EGFP neurons, showing neither a significant de- nor hyperpolarization). F, quantification of the number of elicited action potentials (% of baseline) in response to the depolarizing current injection during baseline recordings and in presence of CRF. G, quantification of the input resistance Rin (CRF, neurons depolarized by CRF; Str I, neurons depolarized by Stressin I; nonR, neurons not affected by CRF). Input resistances are presented for baseline conditions (baseline), during maximal substance effect (substance), and as difference (substance – baseline).
