Figure 7. Synaptic activity in MSNs from WT mice prevents D1R-dependent presynaptic excitation and promotes inhibition through adenosine.
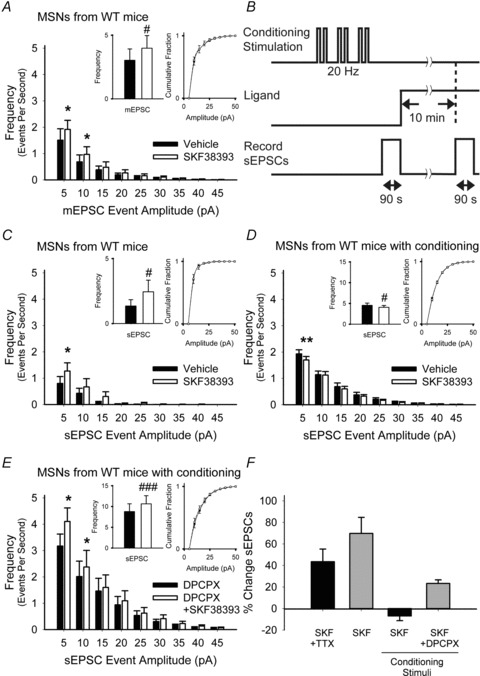
A, SKF38393 increased the average frequency of 5–10 pA and 10–15 pA inward currents and did not alter the mEPSC amplitude distribution. For panels A and C–E, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student's t test with Bonferroni adjustment and #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001, Student's paired t test. B, protocol for synaptic conditioning with cortical stimulation. C, in the absence of conditioning, SKF38393 increased the frequency of 5–10 pA sEPSCs, but had no effect on the cumulative amplitude distribution. D, after conditioning stimuli were applied, SKF38393 reduced the average number of sEPSCs in the 5–10 pA range, but had no effect on their amplitude distributions. E, when the adenosine receptor antagonist DPCPX was applied along with conditioning stimuli, SKF38393 increased the average number of sEPSCs with amplitudes of 5–10 pA and 10–15 pA but did not alter their cumulative amplitude distributions. F, summary of changes in mEPSCs and sEPSCs following SKF38393 with and without synaptic conditioning.
