Figure 2. Simultaneous loss of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 reveals two distinct repetitive firing patterns in CP neurons.
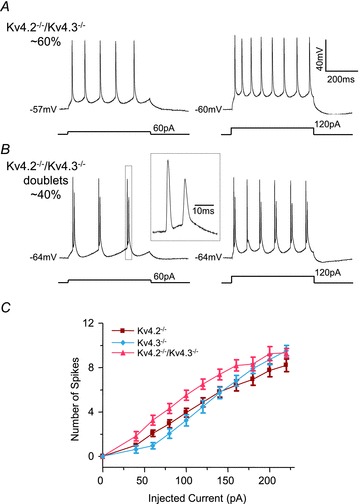
A and B, representative voltage recordings from Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− CP neurons during prolonged (500 ms) depolarizing current injections of varying amplitudes are illustrated. A, repetitive firing of single action potentials was observed in the majority (∼60%) of Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− CP neurons. B, in the remaining (∼40%) Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− CP neurons (Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− doublets), however, action potential doublets were observed. The inset shows the third spike doublet on an expanded time scale. C, mean ± SEM numbers of action potentials evoked in Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− CP neurons (A) during 500 ms current injections are plotted as a function of the amplitudes of the injected currents. Mean ± SEM numbers of action potentials in Kv4.2−/− and Kv4.3−/− CP neurons are replotted from Fig. 1C for comparison purposes. The input–output curve (number of spikes vs. injected current amplitude) for Kv4.2−/−/Kv4.3−/− (n = 16) CP neurons were significantly (P < 0.001) different from those of Kv4.2−/− (n = 30) or Kv4.3−/− (n = 21) CP neurons.
