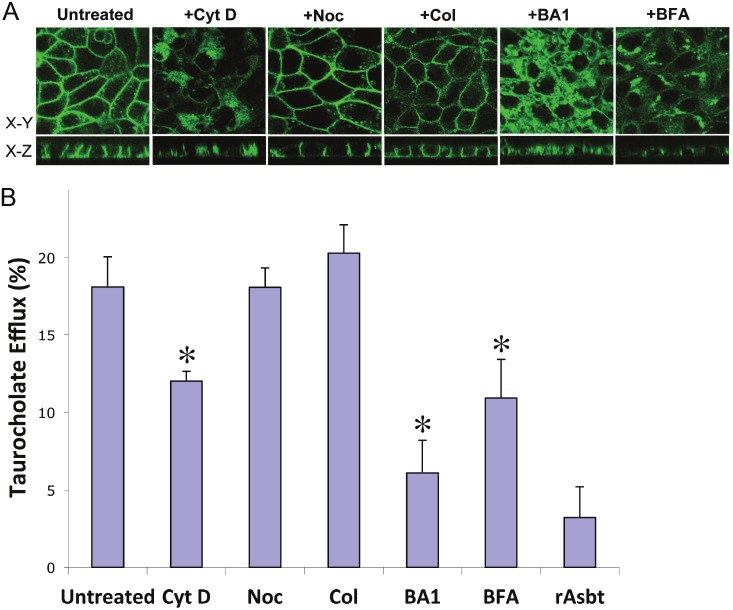
Figure 3.
Effects of biological reagent treatments on cellular distribution and taurocholate (TC) efflux of hOST proteins. The GFP fused hOSTα (α-GFP) constructs were stably co-transfected with hOSTß and rat Asbt in MDCK cells. A: The membrane expression of hOSTα-GFP was detected by confocal fluorescence microscopy and photomicrograph of GFP-fused hOSTα was obtained on a confluent monolayer of the stably transfected MDCK cells cultured on glass coverslips. B: The Na+-independent efflux of taurocholate was examined in the MDCK cells stably transfected with rat Asbt, human OSTα and ß cDNAs. In this model system, the rAsbt acted as an apical bile acid loading pump in the stably transfected MDCK cells. The bile acid efflux activity from the basolateral domain by hOSTα and ß proteins was measured by radioactive scintillation counting. Data are presented as percentage (%) of total TC efflux and represent the mean value ± S.E. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Asterisk (*) for each stably transfected MDCK cells treated with drugs indicates significant difference (p<0.05) from drug untreated cells by unpaired t -test. The stably transfected MDCK cells were treated with 33μM nocodazole (Noc), 10μM colchicine (Col), 2μM cytochalasin D (Cyt D), 50nM bafilomycin A1(BA1), and 2μM brefeldin A (BFA), respectively, at 37°C for 16 hr. (Untreated = drug untreated stably transfected MDCK cells; rAsbt = MDCK cells transfected with rAsbt only).