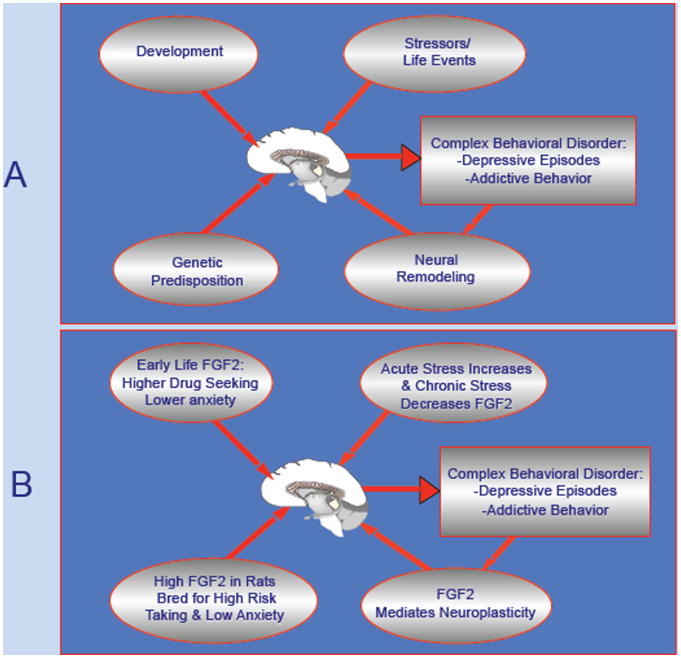
Figure 1. The Role of FGF2 in the Vulnerability to Mood and Addictive Disorders.
Panel A depicts the major factors that converge on the brain to modify vulnerability to complex behavioral disorders such as major depression or substance abuse- Genes, Development, Stress and other Environmental Events all converge at the level of the brain to alter neural circuits that control behavior. Moreover, the behavior itself, such as a depressive episode or a period of substance abuse, in turn modifies the brain through neuroplasticity mechanisms, and increases the likelihood of relapse.
Panel B illustrates the fact that FGF2 has been implicated in each of these mechanisms, with specific examples of its role in each of these domains. Thus, FGF2 plays multiple roles— genetic, developmental, and experiential, in regulating the propensity to certain behaviors such as mood disorders or drug abuse. In general, low FGF2 levels predispose towards depression, while high FGF2 levels predispose towards substance abuse.