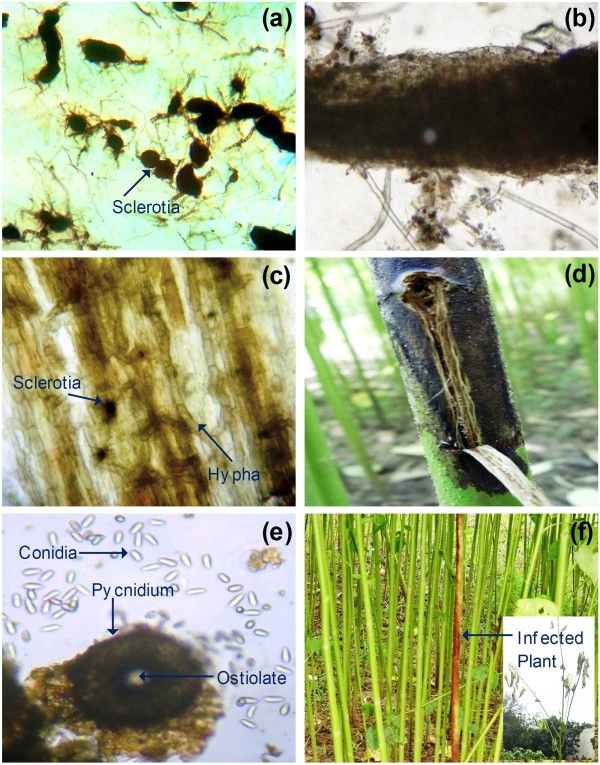
Figure 1.
Infection of jute by M. phaseolina. (a) Stereomicrograph of sclerotia that exists in soil and crop residue. (b) Pathogen produces extensive and profuse aerial hyphae to invade the stem bark. (c) Longitudinal section of stem bark showing inter- and intracellular mycelium and sclerotia. (d) During early rainy season, hyphae penetrate the plant cell wall and produce disease symptoms. (e) Light micrograph of globose ostiolate pycnidia and spores of M. phaseolina. (f) Diseased plants showing infection of the stem, which eventually wilt and prematurely die (Inset).