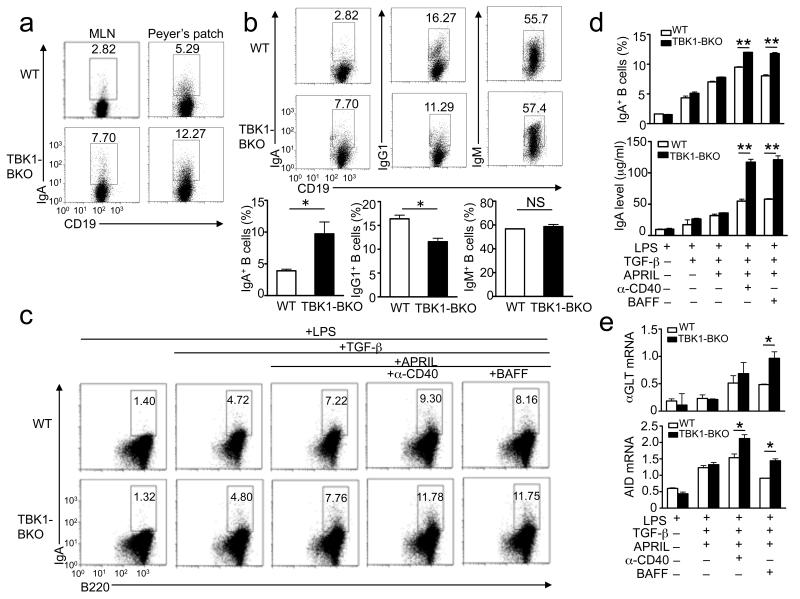
Figure 2. TBK1 negatively regulates IgA class switching induced by TNF family members.
(a) Flow cytometry analyses of the frequency of IgA+ B cells within the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) and Peyer’s patches of non-immunized WT and Tbk1BKO mice (8 months of age). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (b) Flow cytometry analysis of the frequency of IgA+, IgG1+, and IgM+ B cells (within the splenic B cells) of WT and Tbk1BKO mice (6 weeks of age) immunized with SRBC for day 7. Data are presented as a representative plot (upper) and summary graphs (lower) and are representative of three independent experiments. (c, d) Splenic B cells were cultured in the presence of LPS (1 μg/ml), either alone or in combination with other indicated inducers: TGF-β (2 ng/m l), APRIL (200 ng/ml), anti-CD40 (1 μg/ml), or BAFF (200 ng/ml). On day 5, intracellular IgA was quantified by flow cytometry (numbers indicate percentage of IgA+ B cells). Data are representative (c) or summary (d, upper panel) of three independent experiments. The concentration of secreted IgA in the culture supernatants was measured by ELISA (d, lower). Data are presented as mean±SD of three independent experiments. (e) Splenic B cells were cultured as in c and collected on day 4 for αGLT and Aicda QPCR analysis. Actin beta (Actb) was used as an internal control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01.