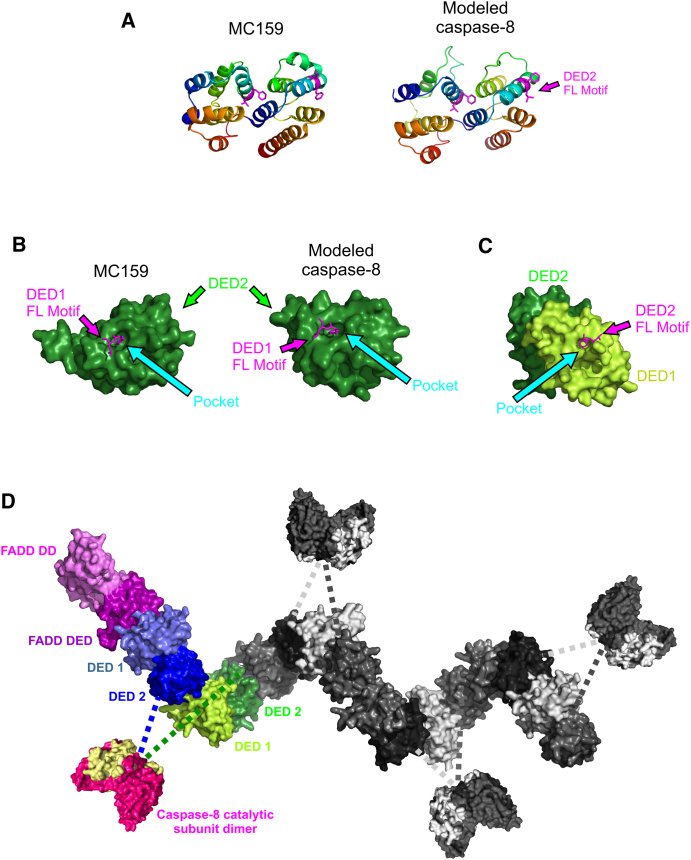
Figure 5.
Structural Modeling of Procaspase-8 DED Chain Formation within the DISC
(A) Published structure for MC159 used by Phyre to structurally model the DEDs of procaspase-8.
(B) Surface structure of MC159 DED2 and modeled procaspase-8 DED2 showing the FL motif from DED1 interacting with a pocket on the surface of DED2.
(C) Modeled surface structure of caspase-8 DEDs showing the pocket in DED1 that could interact with the FL motif from either FADD or DED2 of another molecule. The interaction interface between adjacent tandem DEDs was modeled using the intramolecular interface between DED1 and DED2.
(D) Structural modeling of the interactions that may occur between the DEDs of FADD and caspase-8. Interactions between FADD (structure 2GF5) and procaspase-8 (or between adjacent sets of procaspase-8 DEDs) were modeled using the intramolecular interface between DED1 and DED2, resulting in a DED chain. The colored subunits of the model correspond to the model of the interaction between FADD DED and one dimer of procaspase-8. The extended chain is shown in gray. Catalytic subunit dimers (p182/p102, modeled from structure 3KJQ) are shown to indicate how we would expect antiparallel dimers to form along the length of the DED chain (dotted lines represent the linker between DED2 and p18 subunit of procaspase-8). Note that the helical character of the DED chain is uncertain, since small changes in the interface would significantly change the long-range topology.