Fig. 2.
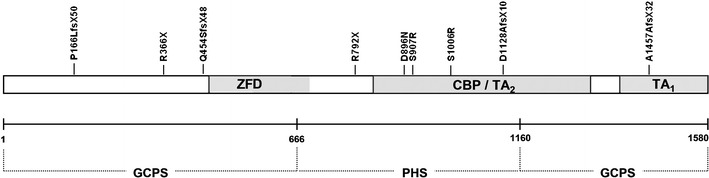
Schematic view of the GLI3 gene structure and overview of all exonic point mutations identified in this study. ZFD, zinc-finger domain [amino acids (aa) 462–645] reported by Ruppert et al. (1990). CBP, CBP-binding domain (aa 827–1,132) reported by Dai et al. (1999). TA2 transactivation domain (aa 1,044–1,322) reported by Kalff-Suske et al. (1999). TA1 transactivation domain (aa 1,376–1,580) reported by Kalff-Suske et al. (1999). GCPS, Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome. GCPS is caused by truncating mutations lying between aa 1–666 and 1,160–1,580 of the protein (Johnston et al. 2005, 2010). PHS, Pallister–Hall syndrome. PHS is caused by mutations affecting the middle third (aa 667–1,160) of the protein (Johnston et al. 2005, 2010)
