Figure 5.
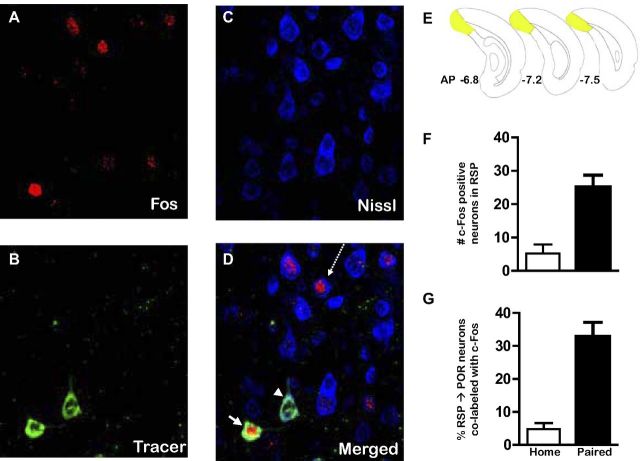
Histochemically verified neurons that project from RSP to POR are activated following fear conditioning. Photomicrographs of dorsal RSP neurons (ipsilateral to the injection site) obtained from sequential scans with a confocal microscope equipped with lasers to detect the c-Fos (A), the CTb-488 tracer (B), and the Nissl labels (C). D, Merged image of the three labels depicted in A–C. The white arrow indicates a neuron (green) that projects from RSP to POR that is immunopositive for c-Fos (red), whereas the projection neuron (green) identified by the white arrowhead is not c-Fos positive. The arrow with the dashed line points to a Nissl-stained RSP cell (blue) that is immunopositive for c-Fos (red). This neuron (blue) was not retrogradely labeled, indicating that it does not project to POR. E, Brain diagrams reflecting the rostrocaudal location from which the confocal images of RSP neurons were collected. F, Average (mean ± SEM) c-Fos expression in RSP in home cage (n = 3) compared with fear-conditioned (n = 5) rats. G, Average (mean ± SEM) percentage of RSP neurons that project to POR that are immunopositive for c-Fos.