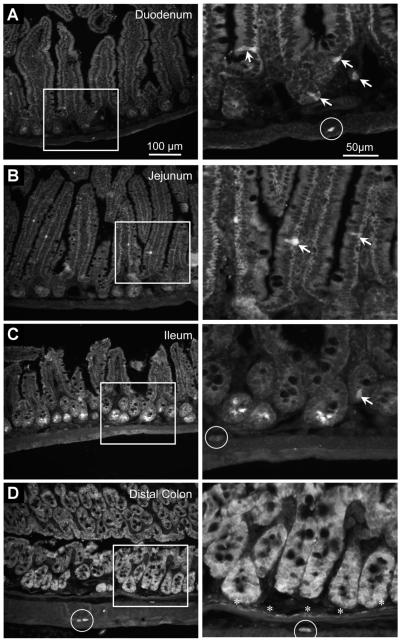
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs of sections from a 5-HT4R(BAC)-eGFP mouse showing GFP immunoreactivity in the (A) duodenum, (B) jejunum, (C) ileum, and (D) distal colon. White boxes indicate regions shown at higher magnification. In the duodenum and jejunum, GFP immunoreactivity was detected in enteric neurons (circle) and enteroendocrine cells (arrows). In the ileum, GFP immunoreactivity was detected in epithelial cells at the base of crypt glands, in enteroendocrine cells, and in neurons. In the distal colon, GFP immunoreactivity was observed throughout the epithelial layer, in a monolayer of cells along the muscularis mucosa (asterisks), and in neurons (circles).