Figure 3.
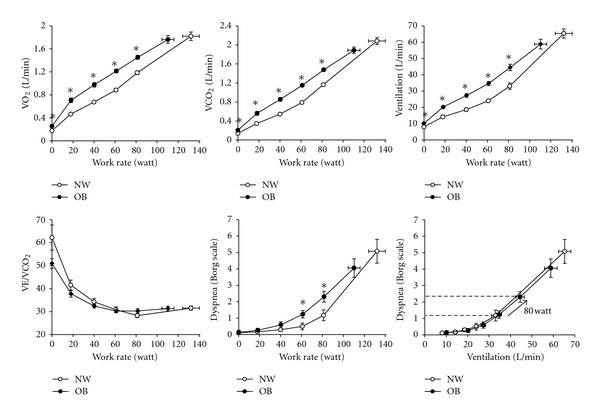
Oxygen uptake (VO2), carbon dioxide output (VCO2), minute ventilation (V E), the ventilatory equivalent for CO2 (V E/VCO2), and dyspnea intensity are shown to be relative to cycle work rate in normal weight (NW) and obese (OB) women. Relationships between dyspnea intensity and ventilation during exercise were similar in OB and NW, thus, increased dyspnea ratings at a given work rate in OB reflected the higher ventilator requirements at that work rate. Values are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 OB versus NW at a given work rate. Data from Ofir et al. [11].
