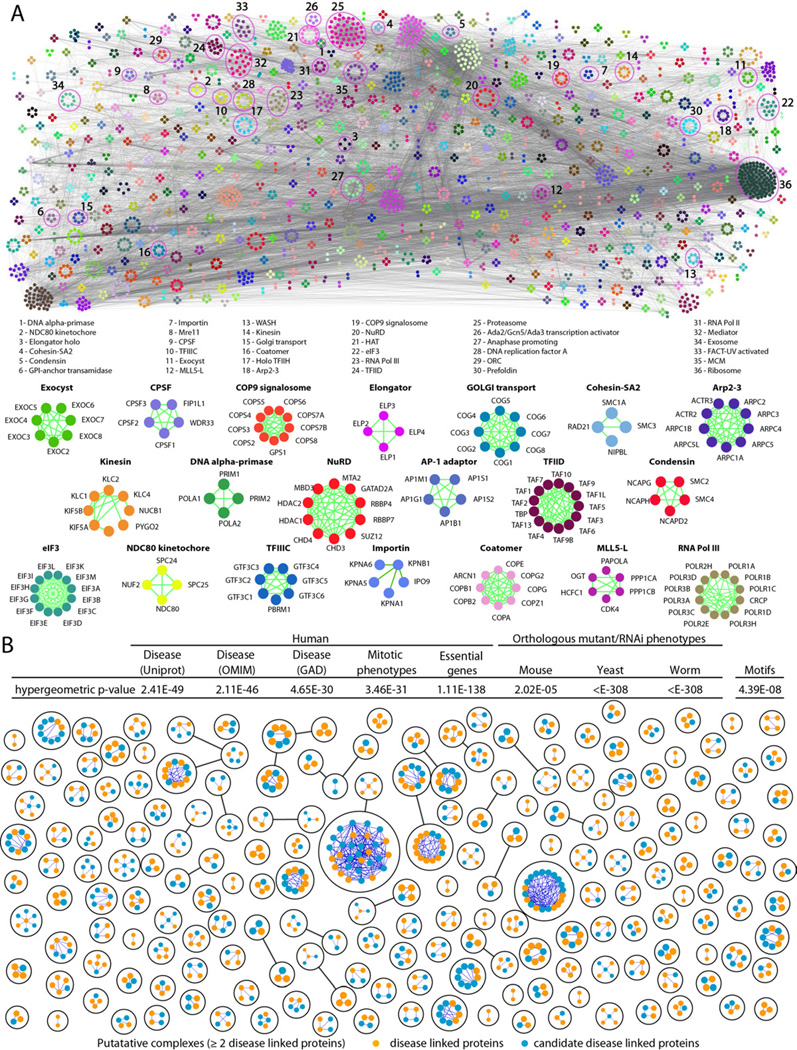
Figure 4. Global map of high confidence human protein complexes.
A- Schematic of the global network of inferred human soluble protein complexes (colored by membership), with representative examples and supporting PPI highlighted. B- Putative complexes with 2 or more components with human disorder associations annotated in UniProt (The UniProt Consortium, 2011), Online Inheritance of Man (OMIM)(Hamosh et al., 2005) or the Genetic Association Database (GAD)(Becker et al., 2004). Inset table shows highly significant interaction overlap (i.e., shared annotated edges) with phenotypic datasets that reveals protein subunits of the same predicted human complex tend to exhibit similar disease and genetic associations in human populations (see Extended Experimental Procedures), RNAi phenotypes in cell culture (Neumann et al., 2010), mutational and RNAi phenotypes in other species (via orthology), and shared transcriptional regulatory motifs (Xie et al., 2005). See also Figure S4C, and Table S4.