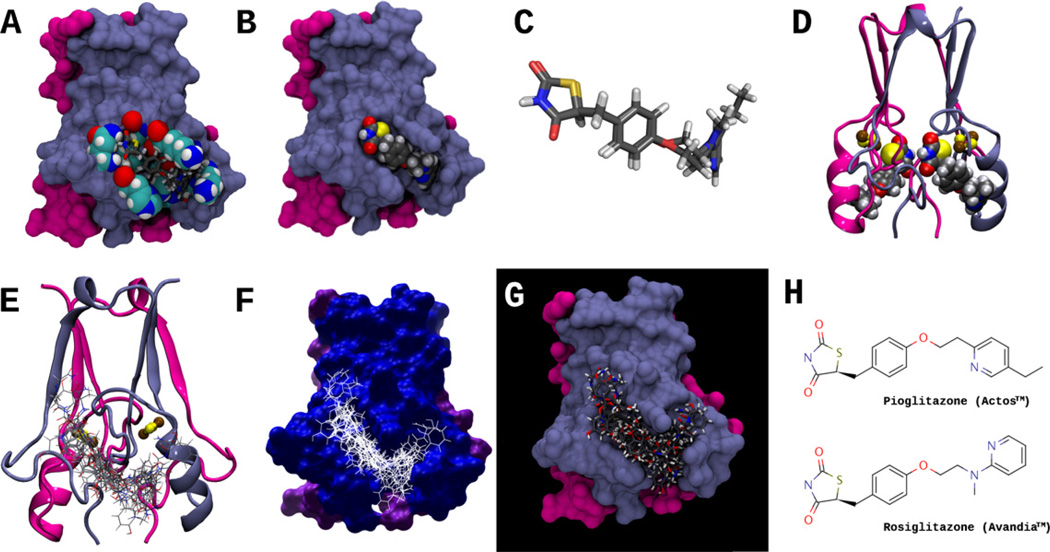
Fig. 3.
(A) Molecular surface representation of the MitoNEET homodimer; residues that interact with both pioglitazone and rosiglitazone are shown in space-filling representation, and include His48, Ile49, Gln50, Arg76, Lys78, Ala86, Lys89, and His90. Both pioglitazone and rosiglitazone are shown as licorice models, docked in the predicted binding conformation found using AutoDock Vina. Protomer I of the mitoNEET homodimer, is colored light blue, and protomer II is colored magenta. (B) Surface representation of MitoNEET homodimer, showing rosiglitazone docked (space-filling representation) in the MitoNEET binding pocket. (C) Superposition of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in their docked conformations, as in (A); note that conformations of the TZD ring is nearly identical for both molecules. (D) Ribbon representation of the MitoNEET-rosiglitazone complex, showing rosiglitazone docked to both MitoNEET protomers; the 2Fe–2S clusters are shown in balls and sticks, where iron and sulfur atoms are colored brown and yellow, respectively. (E–G) Ribbon and surface representations of MitoNEET and an ensemble of 17 docked ligands (interactions shown in Fig. 5). (H) The structures of Pioglitazone (Actos™) and Rosiglitazone (Avandia™). Pioglitazone was the first ligand shown to bind to MitoNEET [1].