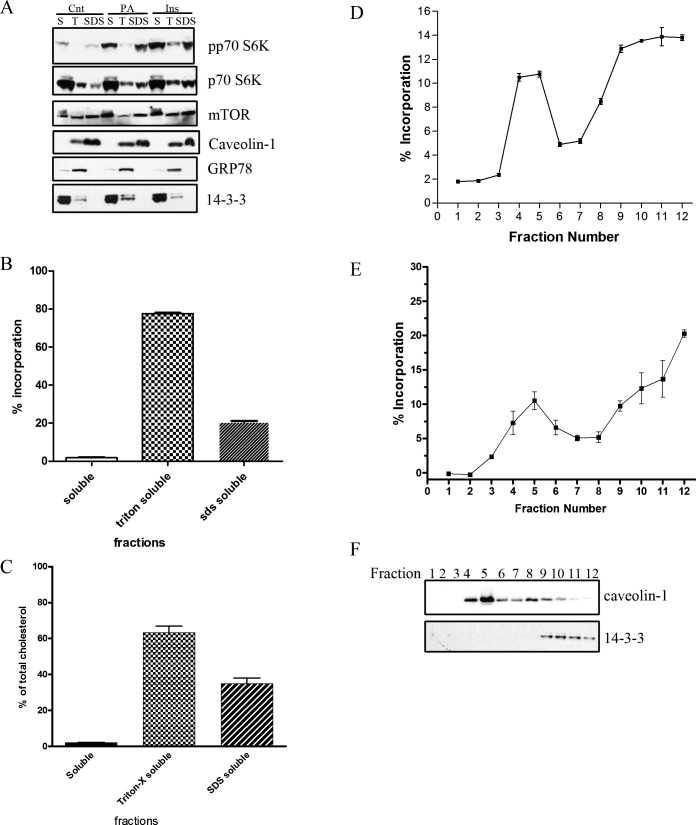
Figure 4. .
PA- and insulin-induced mTOR signaling is regulated within lipid microdomains. (A) Treated R28 cells were fractionated at 100,000g, to which the pellet was extracted with 1% Triton-X and spun again at 100,000g. The resultant pellet was resuspended in 1% SDS. The fractions, cytosolic/soluble (S), TritonX-100 soluble (T), and SDS solubilized (SDS) were analyzed by Western blotting for various mTOR signaling elements (p70 S6K and mTOR), and fractionation control proteins (caveolin-1 [24 kDa], GRP78 [78 kDa], and 14-3-3 [28 kDa]). Blots are representative of four independent biologic experiments. Similarly, these fractions were analyzed after treatment with NBD-labeled PA (B) and for cholesterol content (C, data obtained from n = 3 independent biologic experiments). Similarly, low buoyant fractions were isolated from R28 cells in a sodium carbonate sucrose gradient after treatment with an NBD-labeled PA (D) or 14C-labeled PA (E, data obtained from n = 4 independent biologic experiments). Successful fractionation was assessed by performing Western blots for caveolin-1 and 14-3-3 on the sucrose gradient fractions (F, representative blot of at least four independent experiments).