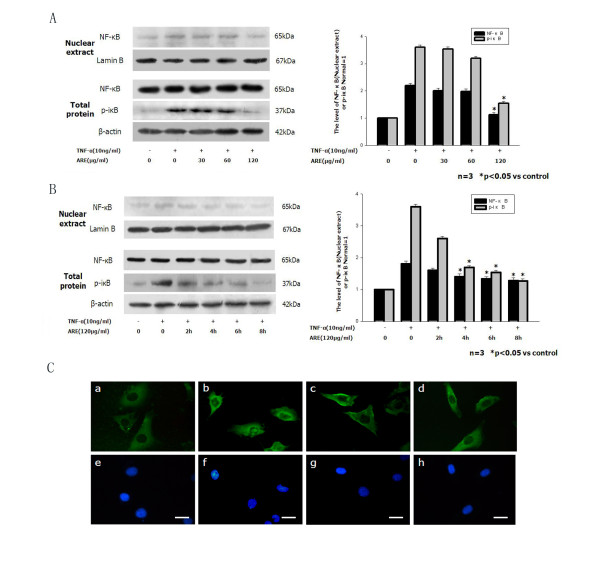
Figure 3.
ARE inhibited TNF-α induced upregulation of NF-κB expression (western blot) and translocation (immunofluorescence staining). A. Confluent SVEC cells were incubated with medium or 10 ng/ml TNF-α alone, or with 10 ng/ml TNF-α together with 30, 60 or 120 μg/ml ARE for 4 h. B. Confluent SVEC cells were preincubated with 120 μg/ml ARE for 2, 4, 6, or 8 h, and thereafter washed and incubated for 4 h with 10 ng/ml TNF-α. NF-κB levels were normalized to the levels of β-actin. C. ARE inhibited TNF-α-induced NF-κB translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in SVEC cells. SVEC cells were cultured on glass coverslips in six-well plates for 2 days, and then incubated with medium (control), 120 μg/ml ARE, or TNF-α (10 ng/ml) alone, or TNF-α in combination with ARE for 4 h. After stimulation, the cells were washed, fixed and permeabilized. The cells were then blocked with 2 % bovine serum albumin in PBS solution, and incubated with a mouse monoclonal NF-κB p65 antibody, followed by a second fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibody. Nuclei were stained with DAPI, and stained cells were assessed by fluorescence microscopy. Immunofluorescent images shown in a–h are representative of at least three experiments with determinations made in quadruplicate. a, untreated control cells; b, cells treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) alone; c, cells treated with ARE (120 μg/ml) alone; d, cells treated with TNF-α plus ARE; e–h, nuclei. Scale bars: 10 μm.