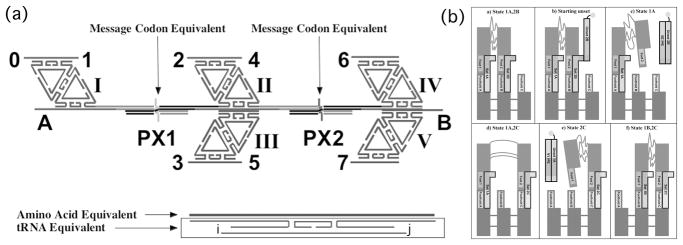
Fig 7.
Advanced Devices Built from DNA. (a) A translation device. The diamond on the left and the double diamonds in the center and on the right are separated by two PX-JX2 devices. The Arabic numerals indicated sticky ends. The sticky ends at the top will bind a DX molecule complementary to the numbers. As shown, a DX with sticky ends complementary to 1 and 2 and another with sticky ends complementary to 4 and 6 will bind. If the device on the right is switched to the JX2 state, a DX complementary to 4 and 7 will bind. This arrangement allows for positional ligation of the DX molecules bound there. The set strands correspond to an mRNA codon, and the bottom sticky ends (i and j) of the DX are the equivalent of the anticodon. The top strand of the DX is equivalent to the amino acid of an aminoacyl tRNA. (b) A bipedal walker. The parts of a walk are shown. The unset strand removes the set strand of the right foot, and then another set strand fastens it to a new position on the sidewalk. The unset strand of the left foot then frees it and it is fastened by a new set strand to the position where the right foot was bound.