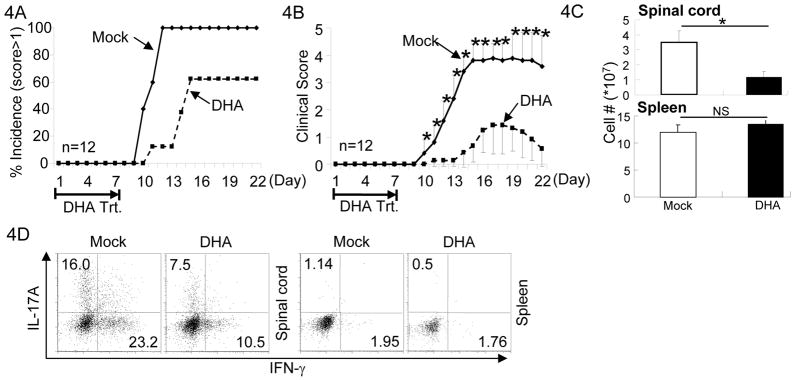
Figure 4. DHA treatment prevented the onset of EAE.
4A. EAE was elicited in mice with MOG/CFA injection. Mice were also treated with DHA (dashed line) or Mock (solid line) during the first 7 days of EAE elicitation. Incidence of the mice showed clinical scores higher than 1 were recorded. Results of 12 mice in one experiment of three are shown.
4B. As described in (A), mice were injected with MOG/CFA to elicit EAE and treated with DHA (dashed line) or Mock (solid line). Clinical scores were recorded every day thereafter. Mean clinical scores ± SEM of 12 mice in one experiment of three are shown (*P<0.05).
4C. As described in (A), mice were injected with MOG/CFA to elicit EAE and treated with DHA (solid bar) or Mock (open bar). The numbers of lymphocytes infiltrating in the spinal cord (upper panel) and total splenocytes (lower panel) in mice were counted after the treatment. Means ± SD of six mice are shown.
4D. As described in (A), mice were injected with MOG/CFA to elicit EAE and treated with DHA or Mock. Lymphocytes were isolated from the spinal cords and spleens of mice with clinical score of 2. The fractions of IL-17A and IFN-γ producing CD4+ T cells were determined by intracellular staining and flow-cytometry. Results are representative of at least three experiments.