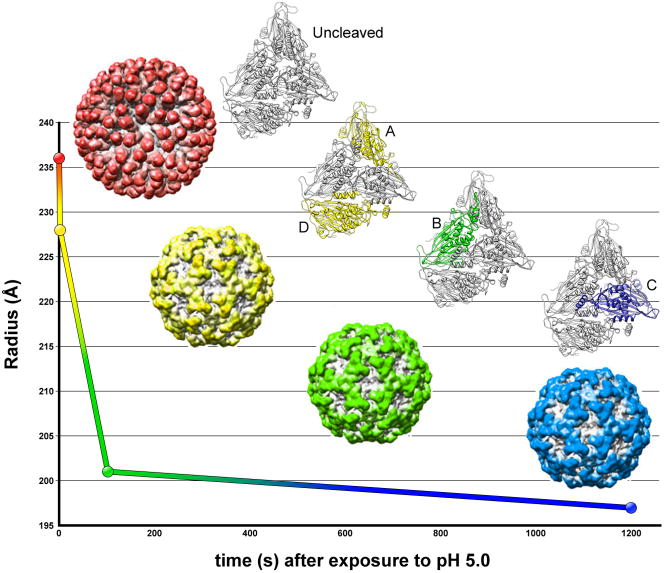
Figure 3.
Maturation pathway of the Nudaurelia capensis ω virus (NωV). Initiating maturation by lowering the pH to 5.0, Matsui et al. used time-resolved SAXS experiments to precisely describe three distinct kinetic stages in the maturation pathway of NωV [44]. The maturation, which involve the autocatalytic cleavage of the C-terminal 74 residues, begins with an initial and dramatic reduction in capsid diameter (red to yellow), which occurs on a millisecond time scale, followed by two progressively slower reductions in size (yellow to green, and then green to blue). Further SAXS experiments showed that homogeneous populations of particles representing each of these intermediates could be attained by analyzing a non-cleaving (Glu73Gln) mutant with cryoEM at specific time points [43]. The reconstructions revealed the underlying mechanism responsible for these transitions. Autocatalytic cleavage occurs initially in subunits A and D (colored yellow in the crystal structure), followed by a slower cleavage of subunit B (green), and a final cleavage of C (blue).