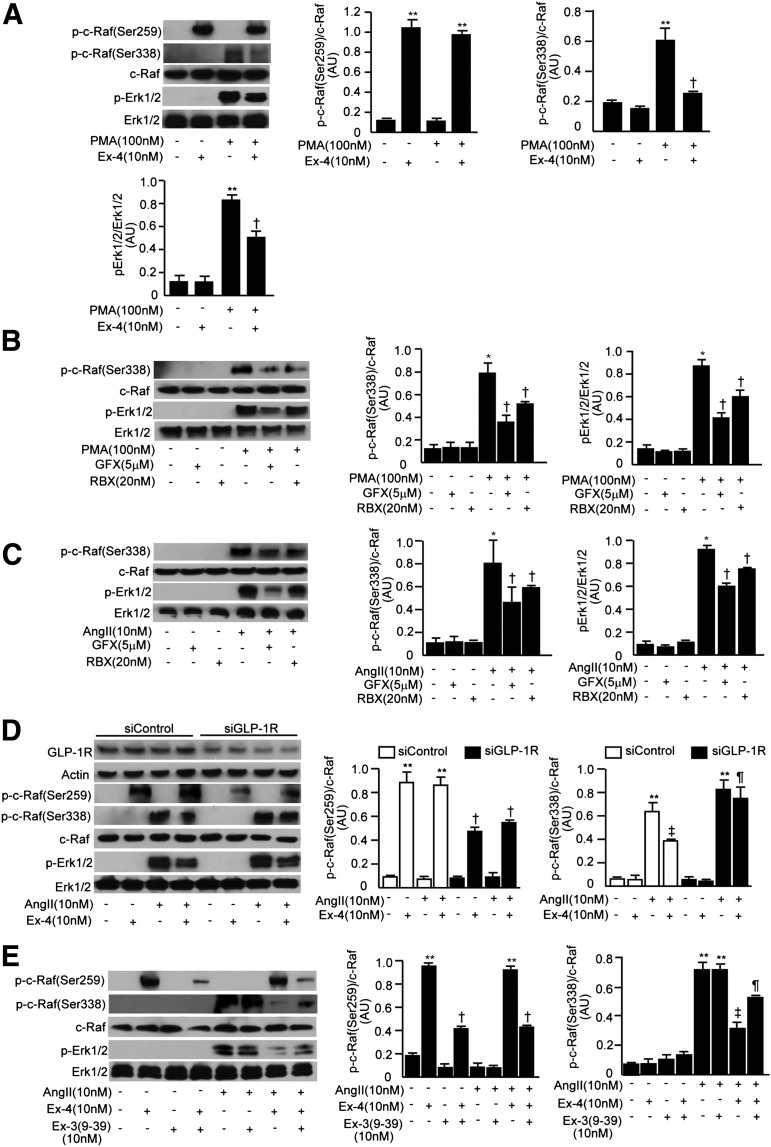
FIG. 6.
Effect of PKC activation (PMA), knockdown, or blocking of GLP-1R on exendin-4 (Ex-4)-stimulated inhibition of Ang II on phospho–c-Raf (p-c-Raf)(Ser338), phospho-Erk1/2 (p-Erk1/2), and PAI-1 activity in RGECs. A: Immunoblots of phospho–c-Raf(Ser259), phospho–c-Raf(Ser338), and phospho-Erk1/2 in RGECs stimulated with PMA (100 nmol/L) in the presence or absence of exendin-4 are shown. **P < 0.001 vs. PMA−/exendin-4− and †P < 0.05 vs. PMA+/exendin-4−. B: Immunoblots of phospho–c-Raf(Ser338) and phospho-Erk1/2 in RGECs stimulated with PMA in the presence or absence of GFX or RBX. *P < 0.05 vs. PMA−/GFX−/RBX−; †P < 0.05 vs. PMA+/GFX−/RBX−. C: Immunoblots of phospho–c-Raf(Ser338) and phospho-Erk1/2 in RGECs stimulated with Ang II in the presence or absence of GFX or RBX. *P < 0.05 vs. Ang II−/GFX−/RBX−; †P < 0.05 vs. Ang II+/GFX−/RBX−. D: Immunoblots of phospho–c-Raf(Ser259), phospho–c-Raf(Ser338), and phospho-Erk1/2 in RGECs transfected with small interfering GLP-1R or small interfering control, stimulated with Ang II in the presence or absence of exendin-4. **P < 0.001 vs. small interfering control/Ang II−/exendin-4−; †P < 0.05 vs. siControl/Ang II−/exendin-4+; ‡P < 0.05 vs. siControl/Ang II+/exendin-4−; ¶P < 0.05 vs. siControl/Ang II+/exendin-4+. E: Immunoblots of phospho–c-Raf(Ser259), phospho–c-Raf(Ser338), and phospho-Erk1/2 in RGECs stimulated with Ang II in the presence or absence of exendin-4 or exendin-3(9-39) [Ex-3(9-39)] are shown. **P < 0.001 vs. Ang II−/exendin-4−/exendin-3(9-39)−; †P < 0.05 vs. Ang II−/exendin-4+/exendin-3(9-39)−; ‡P < 0.05 vs. Ang II+/exendin-4−/exendin-3(9-39)−; ¶P < 0.05 vs. Ang II+/exendin-4+/exendin-3(9-39)−. One of three independently performed experiments is shown. Comparisons were made between groups using either two-sample and paired t tests for two-way comparisons or one-way ANOVA for multiple groups to establish statistically significant differences. Results are expressed as means ± SD. AU, arbitrary units.