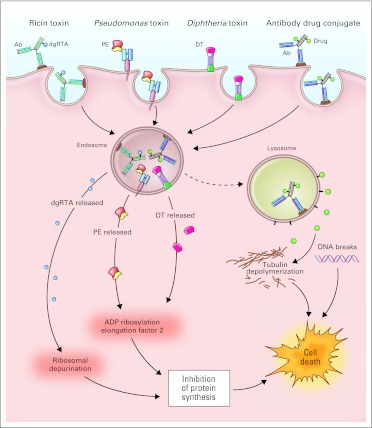
Fig 2.
Mechanisms of action of monoclonal antibody (Ab) conjugates. Monoclonal antibodies and their fragments can be conjugated or linked to cytotoxic agents. Chemotherapy and toxin conjugates must be internalized via receptor-mediated endocytosis, whereas internalization is not required for radioisotope conjugates. After internalization, the active cytotoxic component is released and mediates cell death. Ricin-based immunotoxins depurinate ribosomal RNA and inhibit protein synthesis. Pseudomonas (PE)- and diphtheria (DT) -derived immunotoxins ADP ribosylate elongation factor-2 and inhibit protein synthesis. Antibody drug conjugates mediate cytotoxicity by drug-specific actions (eg, targeting tubulin by maytansin and auristatin, and induction of DNA breaks by calicheamicin). dgRTA, deglycosylated ricin A chain.