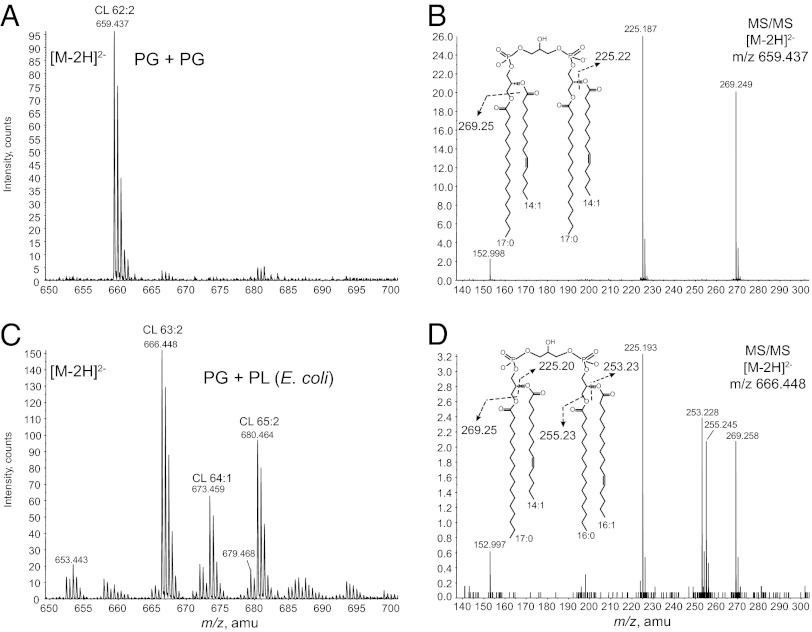
Fig. 6.
YmdB-ClsC differs from ClsA in their substrates. Cell membranes derived from strain BTK29 (∆pgsA, ∆clsABC, ∆ymdB) expressing clsA or ymdB-clsC from plasmid pBAD30 were used with a synthetic PG (17:0/14:1) as substrate to synthesize CL. (A) Membranes from cells with overexpressed ClsA primarily produced a single species of CL consistent with the condensation of two PG molecules. (B) MS/MS spectrum of the [M-2H]2– ion at m/z 659.4 of the CL made by ClsA contained only the carboxylic anions of fatty acids derived from the synthetic PG (17:0/14:1). (C) YmdB-ClsC produced a heterogeneous distribution of CL species. (D) MS/MS spectrum of the [M-2H]2– ion at m/z 666.448 of the most abundant CL formed by YmdB-ClsC contained carboxylic anions of fatty acids derived from both the endogenous sources (16:0/16:1) and those from the synthetic PG (17:0/14:1).