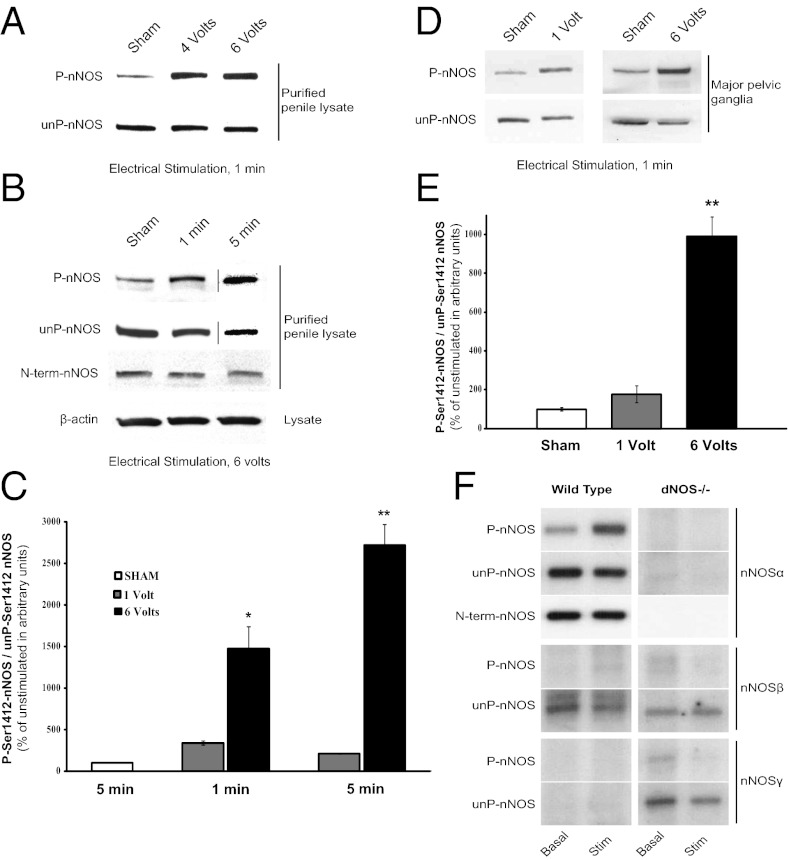
Fig. 1.
Electrical stimulation increases P-nNOS in the penis and MPG. (A) Electrical stimulation of the rat CN causes voltage-dependent increase in penile P-nNOS. (B) The electrically stimulated increase in P-nNOS is also time-dependent, but the total nNOSα detected with an N-terminal antibody is unchanged, showing that nNOS protein is stable during stimulation. (C) Quantification of P-nNOS in arbitrary units is performed by densitometry. Each bar represents mean ± SE of P-nNOS/unP-nNOS expressed relative to unstimulated sham control. (D) Direct electrical stimulation of the MPG also increases P-nNOS in isolated nerve lysates, quantified in E. n = 4–7 animals per condition. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001 compared with sham. (F) Representative blots show differential phosphorylation of nNOS isoforms in wild-type and double nNOS/eNOS- (dNOS−/−) deleted mice after direct MPG stimulation.