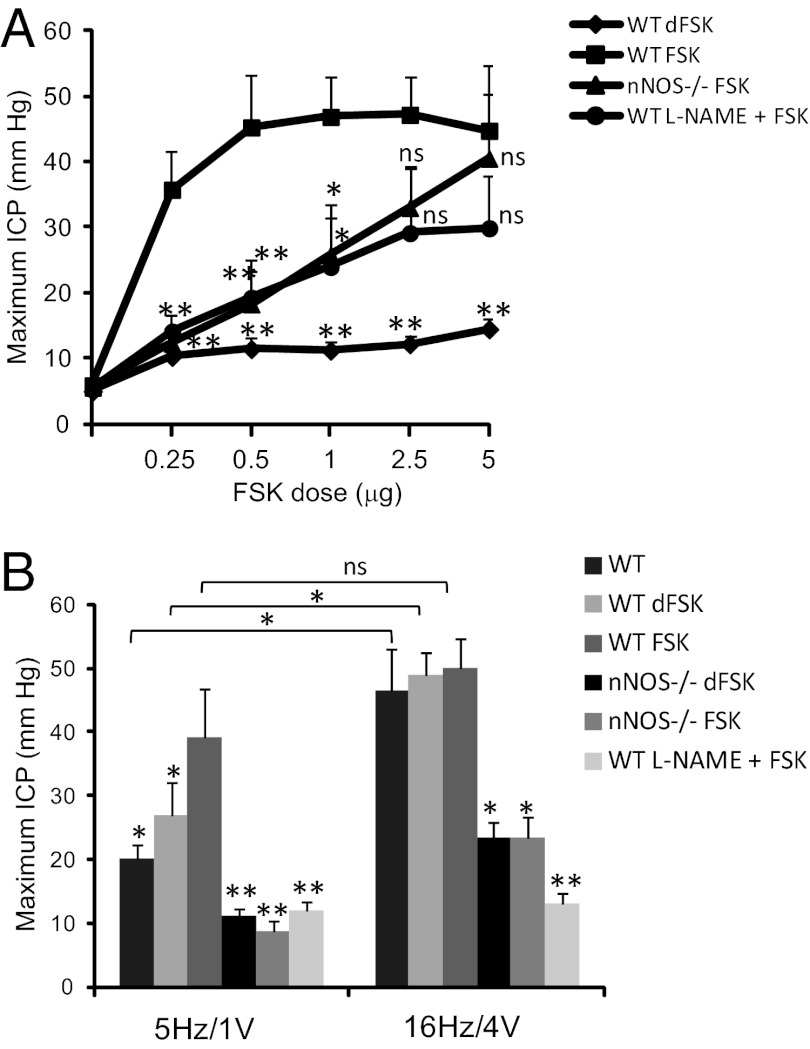
Fig. 5.
nNOS mediates the FSK-induced increase in ICP and enhances the neurogenic erectile response. (A) ICP increases with intrapenile injection of FSK in WT mice. FSK-stimulated ICP is significantly reduced by pretreatment with l-NAME and in nNOSα−/− mice. The inactive compound dFSK does not affect ICP. (B) Immediately following FSK or dFSK treatment, CN electrical stimulation was performed using low (5 Hz/1 V) or maximal (16 Hz/4 V) parameters. Electrically stimulated maximum ICP is similar in untreated wild-type mice and in mice treated with dFSK. FSK injection significantly increases the submaximal electrical stimulation response, but there is minimal response in animals treated with l-NAME or in nNOSα−/− animals. Data are mean ± SE for n = 6–9 animals. *P < 0.05 vs. wild-type FSK; **P < 0.001 vs. wild-type FSK. For 5 Hz vs. 16 Hz comparisons, *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. ns, not significant.