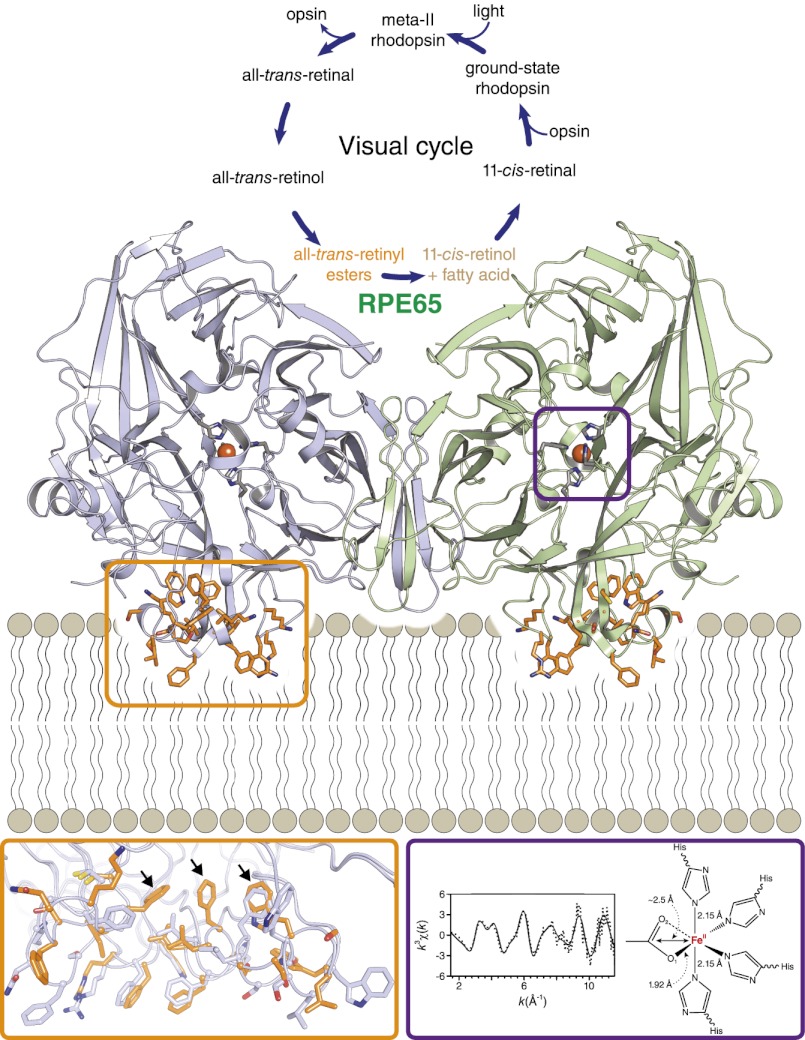
Fig. P1.
Structural insights into the roles of phospholipids and iron in RPE65 enzymology. (Top) Chemical transformations composing the visual cycle. Vision begins when ground-state rhodopsin is converted to activated meta-II rhodopsin by photoisomerization of covalently bound 11-cis-retinal chromophore to the all-trans configuration. RPE65 plays a key role in the regeneration of visual chromophore by catalyzing the isomerization and hydrolysis of all-trans-retinyl esters to form 11-cis-retinol and a fatty acid. (Middle) Dimeric RPE65 complex observed in multiple crystal forms with parallel-oriented membrane-binding surfaces (orange), promoting membrane attachment. (Bottom Left) Structural differences between the lipid-embedded (orange) and delipidated (light blue) structures identified key residues (indicated by arrows) involved in substrate uptake and processing. (Bottom Right) An iron–carboxylate complex identified by X-ray absorption spectroscopy indicates that iron functions as a cofactor to facilitate the retinyl ester hydrolysis step of the retinoid isomerization reaction. His, histidine.