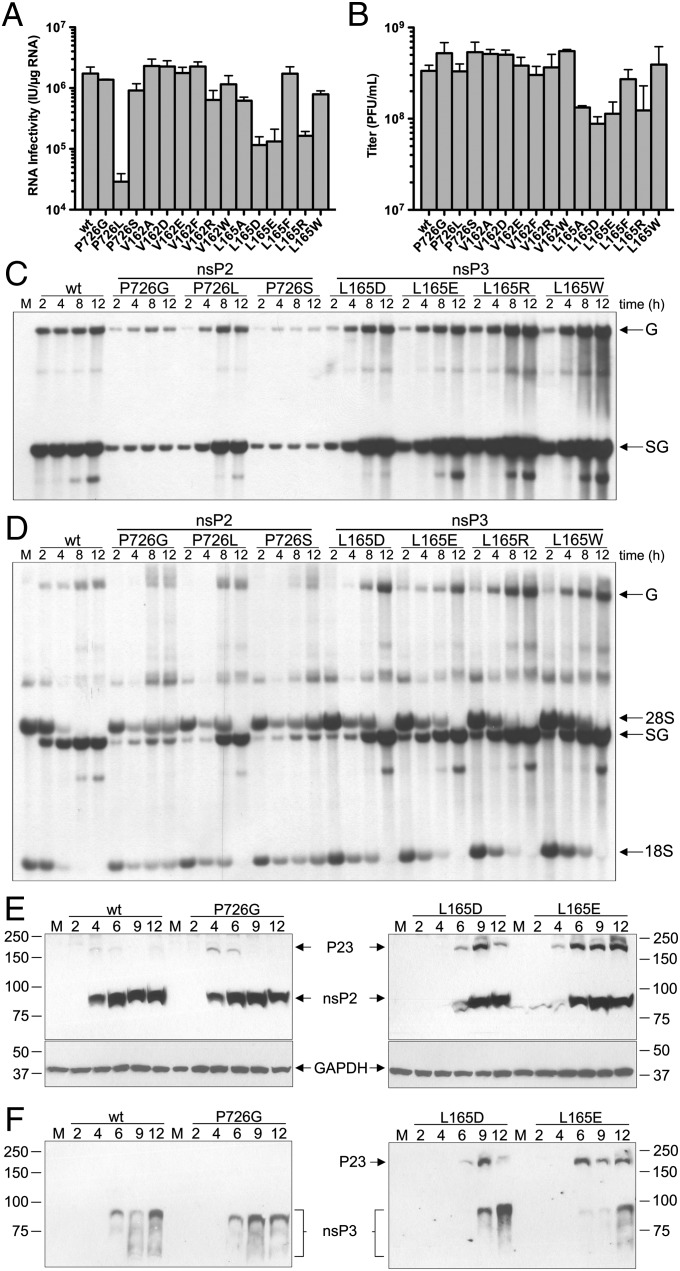
Fig. 3.
In vivo effects of nsP3 linker region mutations. (A and B) Viral RNA infectivity [infectious units (IU)/μg RNA] as measured by infectious center assay (A) and viral titers [plaque-forming units (pfu)/mL] (B) 24 h after electroporation of BHK cells, as determined by plaque assay over two or more independent experiments. Error bars represent the SEM. (C and D) Cells were infected with wild-type or mutant SINV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10. At indicated time points postinfection, RNAs were labeled for 3 h in the presence (C) and absence (D) of actinomycin D. Total RNAs were harvested and analyzed by denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis. The position of genomic (G), subgenomic (SG), 28S, and 18S RNAs are labeled. M indicates mock-infected cells labeled for 3 h. (E and F) Analysis of P23 cleavage of nsP2 P726 and nsP3 L165 mutants in vivo. Total protein was harvested from wild-type and indicated mutant SINV-infected BHK cells at indicated hours postinfection and analyzed by Western blot using anti-nsP2 (E) and anti-nsP3 (F) antibodies.