Fig. 7.
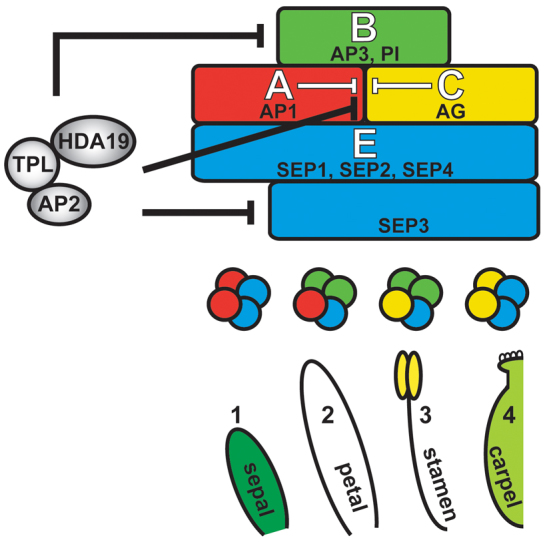
Model of AP2 function during flower development. AP2 controls the outer expression boundaries of B-, C- and E-class genes by recruiting TPL and HDA19. This AP2 repression complex directly represses the C-class gene AG in whorls 1 (sepal) and 2 (petal) and the B-class gene AP3 and E-class gene SEP3 in whorl 1. AP2-mediated repression of the B-class gene PI in whorl 1 may occur through negative regulation of upstream activators, such as SEP3. MADS-domain products of the floral homeotic genes (colored circles) are predicted to interact with one another and with SEP proteins to form quartet complexes that regulate gene expression required for organ identity specification (Honma and Goto, 2001). Intermediary proteins might facilitate TPL and HDA19 association.
