Fig. 1.
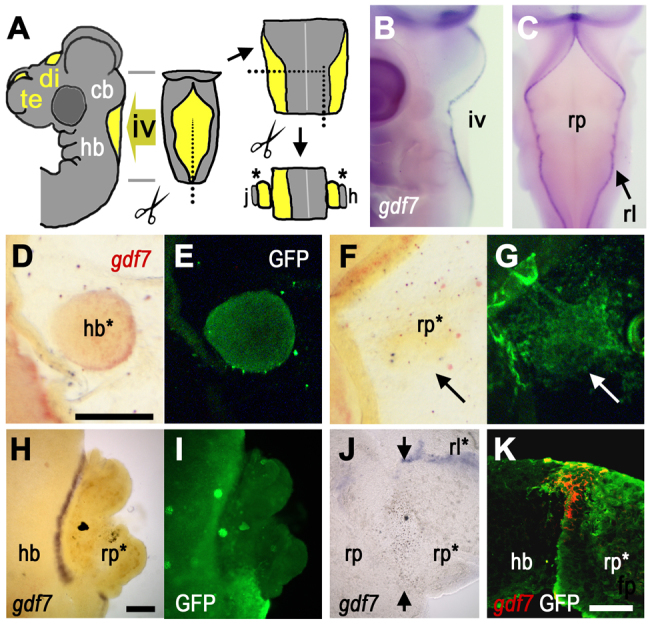
Induction of gdf7 by tissue interactions. (A) Schematic E4 chick head showing ventricles (yellow), which form bilaterally within the forebrain (fb) and at the dorsal midlines of both the diencephalon (di) (third ventricle) and cerebellum (cb)/hindbrain (hb) (fourth ventricle, iv). Tissue surrounding iv was dissected for grafts and co-cultures (j and h are references to J and H). (B,C) In lateral (B) and dorsal (C) views at E4, gdf7 (blue) is expressed at the boundary between hindbrain roof plate (rp) and rhombic lip (rl). (D,E) In ovo graft of GFP-tg hindbrain (hb*) into wild-type roof plate results in gdf7 induction (D, red) around the graft interface after 24 hours (GFP label in E). (F,G) gdf7 is not induced when E4 GFP-tg-roof plate (rp*, G) is grafted into E3 wild-type roof plate (arrow). For this homotypic graft, there is some evident mixing of donor and host cells. (H,I) In vitro roof plate/neuroepithelium co-cultures (E6) show robust gdf7 induction at the interface between GFP-tg hindbrain and wild-type roof plate (rp*, I). (J) Juxtaposition of E6 roof plate tissues (rp/rp*) in co-culture does not induce gdf7 (arrows indicate interface), while gdf7 is maintained in residual rhombic lip (rl*). (K) Confocal optical slice through a transverse section of a hindbrain/roof plate co-culture interface shows that gdf7 expression (red) is confined to GFP-tg-derived roof plate (rp*). Scale bars: 200 μm in D-G; 200 μm in H-J; 50 μm in K.
