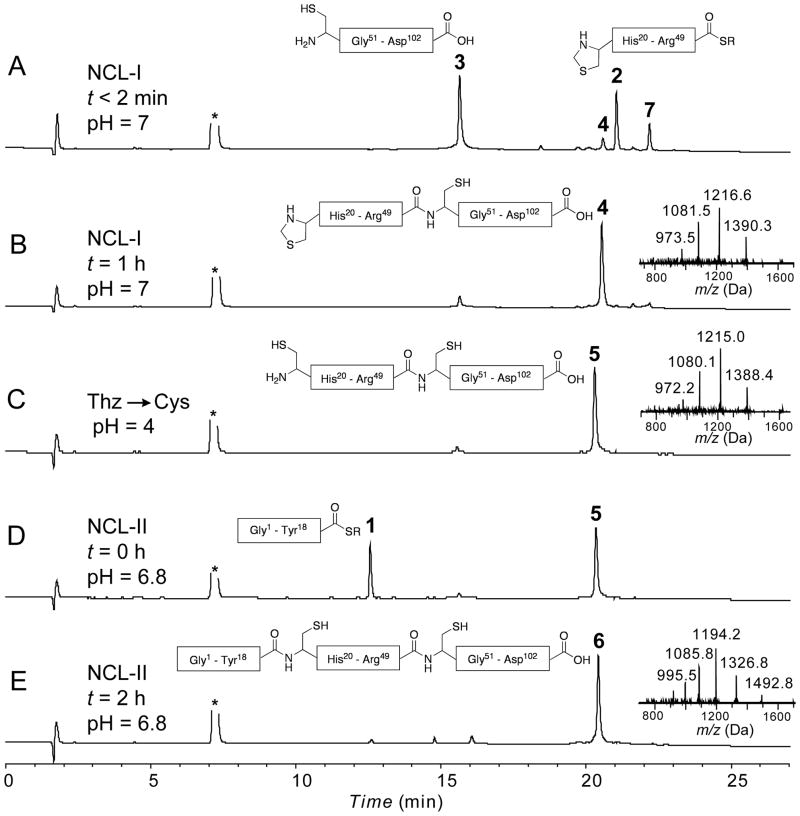
Figure 2.
Analytical LC-MS data for the total chemical synthesis of VEGF. Analytical HPLC profiles (λ = 214 nm) are shown, together with online electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-MS) data (inset) corresponding to each major product. (A) Native chemical ligation between Thz19-Arg49 –αCOSR (2, 15 mg, 3.37 μmol, 1.53 mM) and Cys50̃Asp102̃ COOH (3, 22 mg, 3.66 μmol, 1.66 mM) at t < 2 min. 7 is the intermediate MPAA-exchanged product; (B) Native chemical ligation reaction after 1 h: 4 is the ligation product; (C) Crude reaction mixture after Thz– to Cys– conversion using 60 mM methoxylamine. HCl at pH 4: formation of the desired Cys– product 5 was confirmed by a mass decrease of 12 Da; (D) One-pot native chemical ligation of Gly1-Tyr18 –αCOSR (1, 10.4 mg, 4.39 μmol, 2 mM) and Cys19̃Asp102̃ COOH at t = 0 min; (E) Crude reaction mixture after 2 h at pH = 6.8: 6 is the ligation product Gly1-Asp102-COOH [overall yield (after purification) = 19.3 mg, 1.6 μmol, 48% based on limiting peptide segment 2]. Analytical HPLC was performed using a linear gradient (10̃54%) of buffer B in buffer A over 22 min (buffer A = 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in water; buffer B = 0.08% TFA in acetonitrile) on a C-3 (Agilent), 4.6 °— 150 mm column at 40 °C (flow rate = 1 mL/min). R = -CH2-CH2-SO3H and asterisk (*) corresponds to MPAA.