Figure 4. 2HG-inhibitable H3K9 demethylase KDM4C is required for cell differentiation.
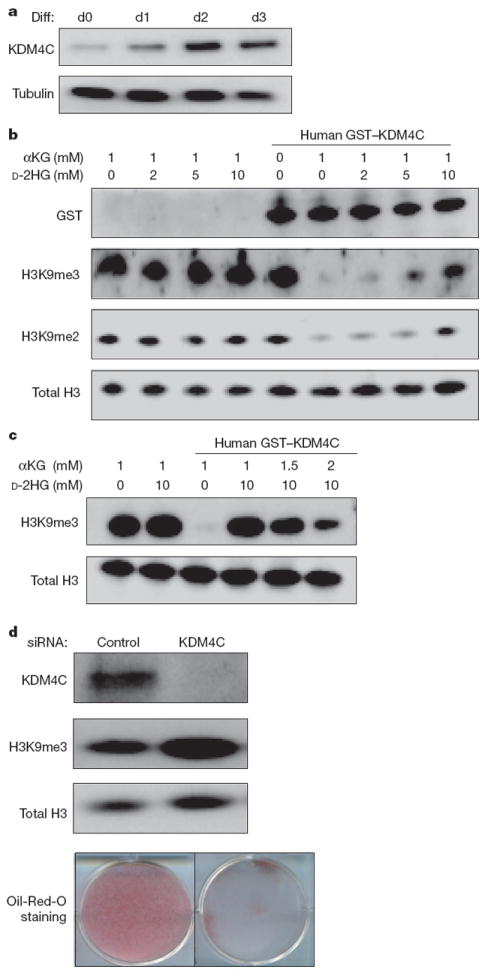
a, 3T3-L1 cells were induced to differentiate (Diff) for 3 days. Before (d0) and each day after differentiation induction, cells were lysed and KDM4C protein levels were assessed by western blotting with specific antibody. Tubulin was used as loading control. b, Bulk histones were incubated with purified GST-tagged human KDM4C in the reaction mix with 1 mM αKG and increasing concentrations of d-2HG. Levels of GST tag, H3K9me3 and H3K9me2 were assessed by western blotting with specific antibodies. Total H3 was used as loading control. c, Bulk histones were incubated with purified GST-tagged human KDM4C in the reaction mix. 10mMd-2HG was added to inhibit the demethylation reaction in the presence of increasing concentrations of αKG. Levels of H3K9me3 were assessed by western blotting with specific antibody. Total H3 was used as loading control. d, 3T3-L1 cells were transfected with control siRNAor siRNA specific for KDM4C. After 3 days, cells were lysed and assessed for expression levels of KDM4C and H3K9me3 by western blotting with specific antibodies. Total H3 was used as loading control. Cells from the same treatment were induced to differentiate for 7 days. The accumulation of lipid droplets was assessed by Oil-Red-O staining. Wells from a representative experiment from a total of three independent experiments are shown.
