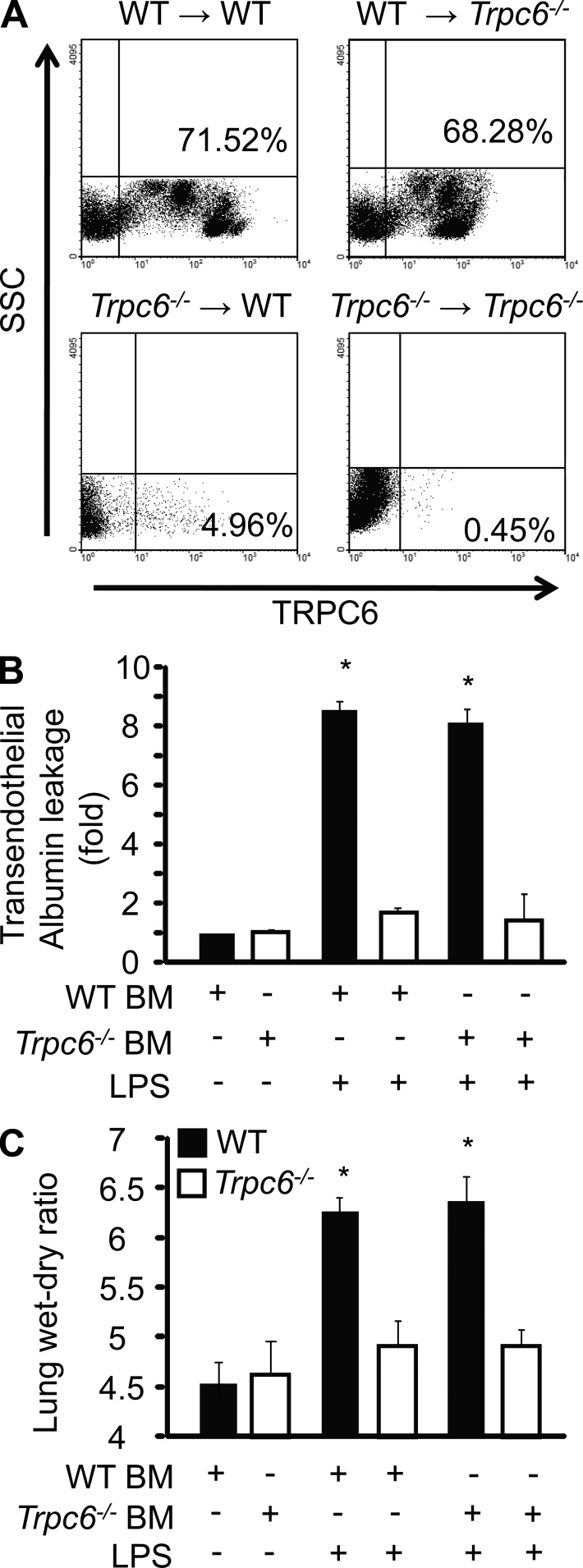
Figure 4.
Effect of BM cells transplantation on LPS-induced increase in lung vascular permeability and edema formation. After irradiation, WT mice were injected with WT or TRPC6−/− BM cells. In parallel, TRPC6−/− mice were injected with WT BM cells or TRPC6−/− BM cells. At 6 wk after BM transplantation, BM cells were isolated from WT or TRPC6−/− chimeric mice, fixed, and incubated with anti-TRPC6 antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody. Data were analyzed using WinMdi software. Dot plots from two such experiments were generated after gating all BM cells from respective groups of mice against side scatter population, as described in Materials and methods (A). Chimeric mice were exposed to nebulized LPS (1 mg/ml) for 1 h. After 3.5 h, Evans blue–labeled albumin was injected retroorbitally into each mouse as described in Materials and methods. Mice were sacrificed at 4 h to determine lung vascular albumin permeability (B), and lung wet/dry ratio (C). Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. * indicates values greater than values in WT or Trpc6−/− lungs without LPS (P < 0.05).