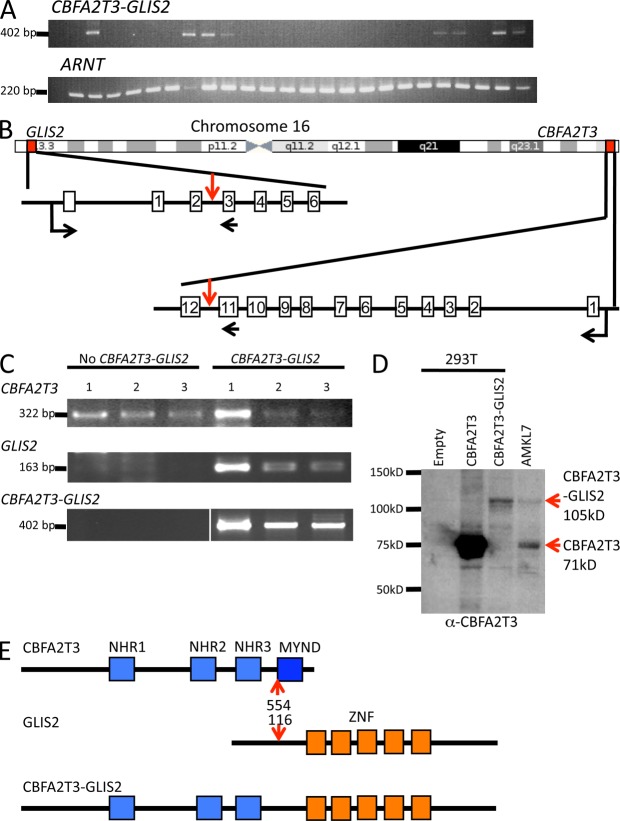
Figure 5.
The CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion is recurrent in AMKL. (A) RT-PCR analysis on a validation cohort of AMKL patients using primers located on CBFA2T3 exon 11 and GLIS2 exon 3 (top). Detection of the ARNT transcript was used as an RNA quality control. (B) Schematic representation of the chromosome 16 chromosomal inversion leading to the fusion between CBFA2T3 and GLIS2. Localizations on chromosome and exon–intron gene structures are indicated. Red vertical arrows indicate the introns targeted by the inversion. Horizontal black arrows indicate localization of the primers used for RT-PCR analysis described in C to detect the fusion transcript. (C) RT-PCR analysis of CBFA2T3 and GLIS2 expression in patients with or without the CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion. White line indicates that intervening lanes have been spliced out. (D) Western blot analysis of AMKL7 cells using an anti-CBFA2T3 antibody. AMKL7 cell lysates were prepared from fresh cells obtained from tertiary recipients. For controls, 293T cells were transfected with empty or CBFA2T3- or CBFA2T3-GLIS2–encoding vectors. (E) Schematic representation of the CBFA2T3, GLIS2, and CBFA2T3-GLIS2 predicted proteins. Red arrows indicate fusion points on each protein. ZNF, Krüppel-like zinc finger domain.