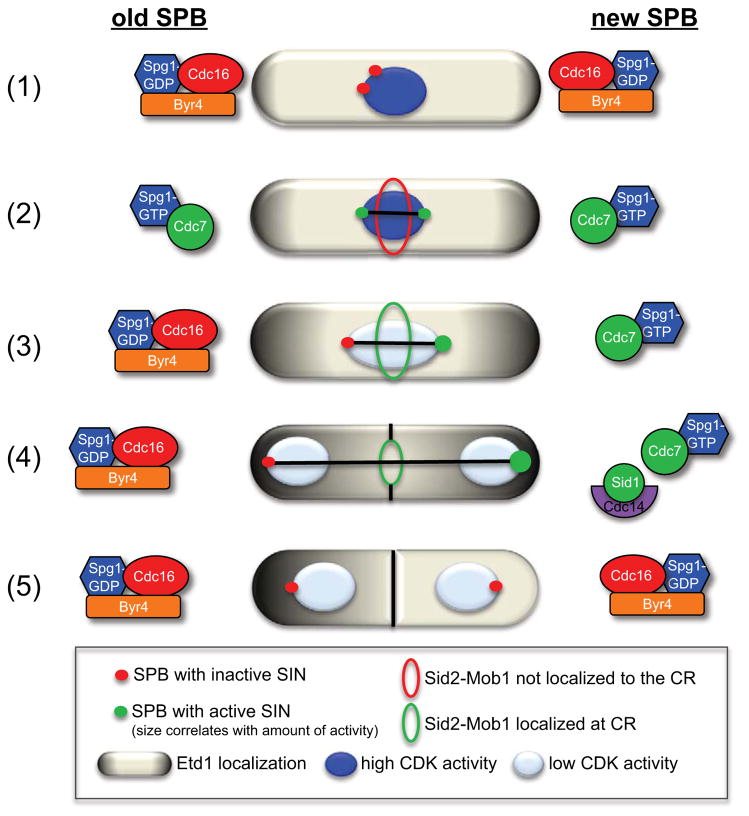
Figure 3.
Localization patterns of the SIN signaling proteins at the ‘old’ and ‘new’ SPBs throughout mitosis. (1) In interphase and early pro-metaphase, Byr4-Cdc16 localize to both SPBs and maintains Spg1 in its GDP-bound inactive state. (2) Then, in late pro-metaphase to metaphase, Cdc7 localizes to both SPBs via interaction with Spg1-GTP. (3) As the spindle begins to elongate in anaphase, Cdc7 disappears from the ‘old’ pole and Byr4-Cdc16 returns to the ‘old’ pole to inactivate the SIN and establish SIN asymmetry. (4) Later in mitosis when CDK activity is low, Sid1-Cdc14 localizes to the ‘new’ SPB with active SIN signaling and as the SPBs reach the cell cortex, Etd1 contacts Spg1 and further activates the SIN on the ‘new’ pole. Since Spg1 is bound to the inhibitory GAP complex (Byr4-Cdc16) on the ‘old’ pole, Etd1 is probably prevented from contacting Spg1 on the ‘old’ pole. Once the spindle is fully elongated, Sid2-Mob1 translocates to the division site and induces CR constriction. (5) After septation, Etd1 disappears from the cell compartment with active SIN signaling and Byr4-Cdc16 returns to this SPB to terminate SIN signaling.