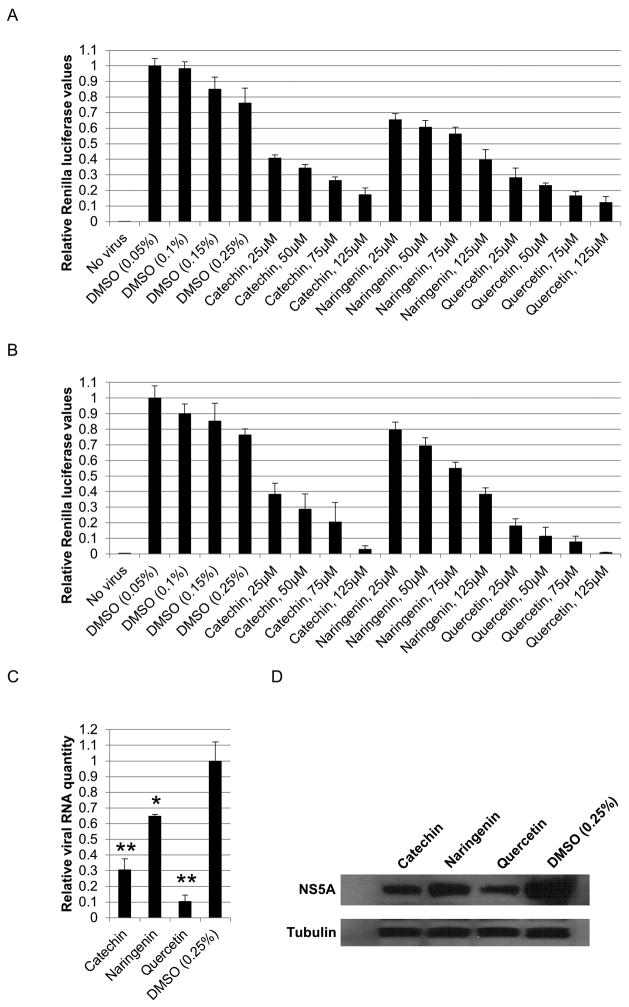
Figure 4.
Dose dependent antiviral activity of catechin, naringenin, and quercetin. A. Huh-7.5 cells were infected with the Renilla reporter virus and immediately treated with a concentration range of 25-125μM of each bioflavonoid for 72 hours, followed by measuring luciferase activity. B. Luciferase assays performed on cells infected with the concentrated supernatants of the cells in figure 4A. Huh-7.5 cells were infected with supernatants and harvested 72 hours later. C. Bioflavonoid effect on viral genome levels. Huh-7.5 cells were infected with the reporter virus and treated with 125μM bioflavonoid for 72 hours followed by quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR. D. Bioflavonoid effect on viral protein levels. Western analyses for NS5A and loading control tubulin was performed the same samples from part C. (* and ** indicate P<0.05 and P<0.005, respectively. Error bars reflect standard deviation.)