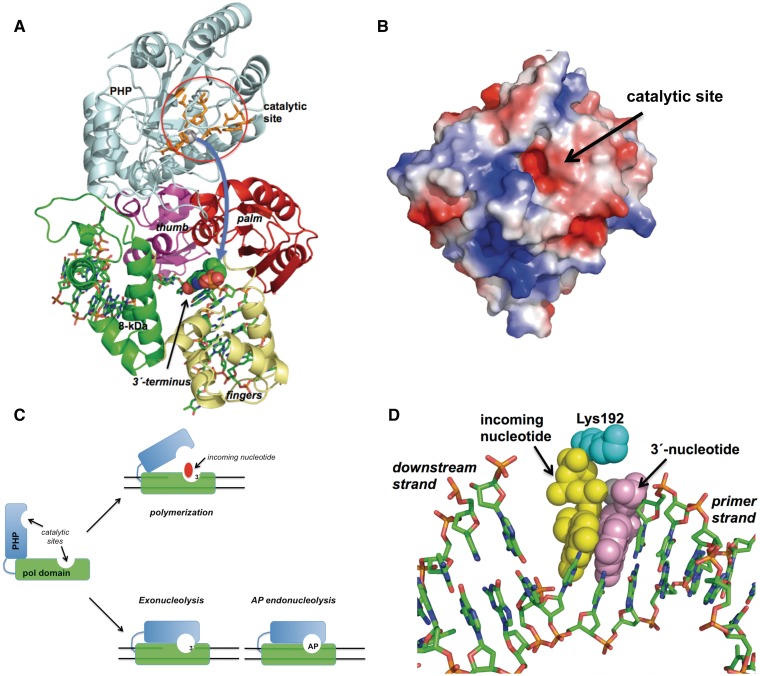
Figure 8.
(A) Model of the PHP motion. The PHP and polymerization subdomains are coloured as in Figure 7A. Catalytic residues of the PHP domain are represented as orange sticks. The 3′ terminal nucleotide of the upstream primer strand is represented as spheres. Curved arrow indicates the proposed movement of the PHP domain. See main text for details. (B) Electrostatic surface of the modelled PHP domain of PolXBs. Superficial placement of the catalytic active site is indicated. (C) Scheme depicting the proposed PHP motion during the 3′-5′ exonucleolytic removal of mispaired 3′ termini and the repair of AP sites by PolXBs. PolX core and PHP domains are represented as green and cyan boxes, respectively. See main text for details. (D) Modelling of the PolXBs residue Lys192 at the polymerization active site. Incoming nucleotide, 3′ primer-terminus and Lys192 are represented as yellow, violet and cyan spheres. Figure was made using PyMOL software (http://www.pymol.org).