Figure 4.
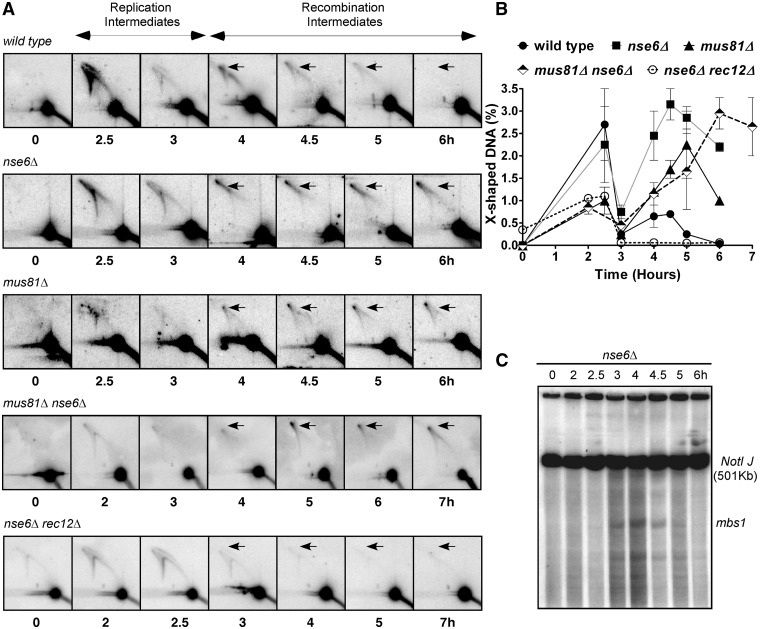
Joint molecules accumulate during meiosis in the nse6Δ mutant. (A) Diploid pat1-114 wild-type (GP6656), nse6Δ (GP6234), mus81Δ (GP6657) and nse6Δ mus81Δ (GP7765) and haploid pat1-114 nse6Δ rec12Δ (GP7773) strains were induced for meiosis. DNA was extracted at the time indicated and digested with PvuII to generate 11.2 kb DNA fragments containing mbs1 (Figure 3B). Branched DNA molecules were assayed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (8,88) in which the first dimension slowly separates DNA primarily by mass and the second dimension primarily by shape, as branched structures have less mobility than linear DNA, and subsequent Southern blot hybridization. DNA from 2.5–3 h shows branched DNA structures arising from replication, while at 4 h, the structures are primarily recombination intermediates (8). Note that X-shaped DNA (arrows) forms in the wild-type at 4 h and disappears by 6 h, as expected for HJs that form and are resolved during the repair of DSBs, but form and persist in nse6Δ, mus81Δ and nse6Δ mus81Δ mutants. (B) Quantification of the X-shaped DNA observed in (A). Each datum is the mean of two independent experiments, with the error bars indicating the range. (C) Meiotic DSBs arise and disappear with wild-type timing in a diploid nse6Δ strain GP6234. DNA prepared at the indicated time after induction of meiosis was digested with NotI, separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Southern blot hybridization with a probe specific to the left end of the 501 kb NotI fragment J, which contains mbs1 near its middle. Note that DSBs appear after replication at 3 h, reach a maximum at 4 h and are mostly repaired by 5 h, consistent with previous results from wild-type and mus81Δ strains (8,9,68,69) and with the timing of HJ formation observed in (A).