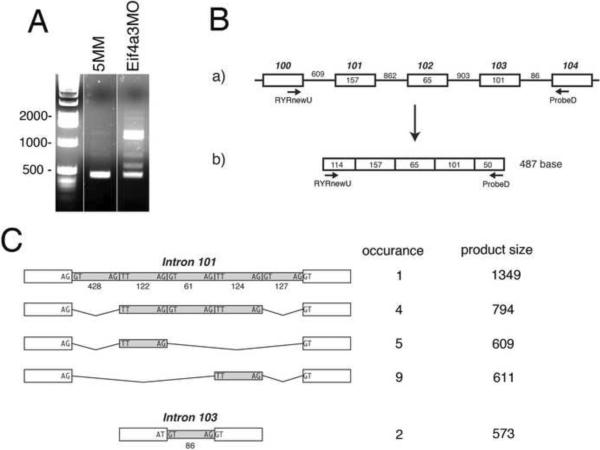
Fig. 5.
Eif4a3 is required for correct splicing of ryanodine receptor (ryr) pre-mRNA. (A) RT-PCR analysis of ryr RNA from Eif4a3MM (5MM) and Eif4a3MO-injected stage 27 embryos; primer pairs are indicated in (B). 29 cycles of PCR was used for this analysis, and samples were not normalized. (B) a) Intron-exon configuration of the X. laevis ryanodine receptor gene from exons 100 to 104. Exons and introns are represented by boxes and lines, respectively; exon size is given in boxes and intron size is given above lines. Exon number is indicated above the boxes, and is based on the X. tropicalis ryr sequence. b) Expected RT-PCR product after complete splicing. (C) Observed retention patterns of introns 101 and 103. PCR products from Eif4a3MO-injected embryos that were larger than 487bp were cloned and sequenced. The schematic shows the four identified retention patterns of intron 101. For intron 103, only complete retention was observed. The size of each intron subdomain is indicated. Sequences of exon-intron and intron subdomain boundaries are indicated.