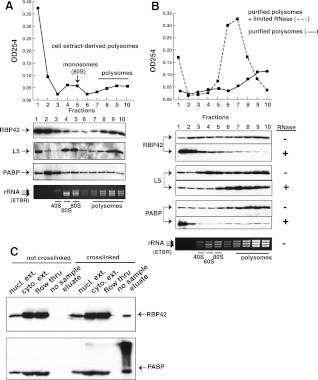
FIGURE 4.
RBP42 fractionates predominantly with polysomes. (A) Polysome fractionation profile is shown. Immunoblotting of fractionated material was accomplished using the RBP42, L5, and PABP antibodies listed on the left side of the panel. L5, a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit, is a monosome (80S) and polysome marker; PABP, a cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding protein, is an mRNA marker. Locations of the small subunit (40S), large subunit (60S), intact monosomes (80S), and polysomes in the gradients was accomplished using an ethidium bromide (ETBR)–stained Agarose gel. T. brucei 28S is naturally present as two large fragments, which migrate below 18S rRNA. (B) Purified polysomes obtained from fractions 7–10 in A were further fractionated after mock (solid line) or limited RNase A treatment (dotted line). Immunoblotting was done as shown in A. (C) Immunoblotting of fractionated lysates before or after in vivo protein–RNA crosslinking by UV light. An equal amount of each fraction was present in all lanes to show the relative abundance of RBP42 and PABP in each fraction. Fractions, defined at the top of each lane, were obtained after oligo-d(T) cellulose chromatography.