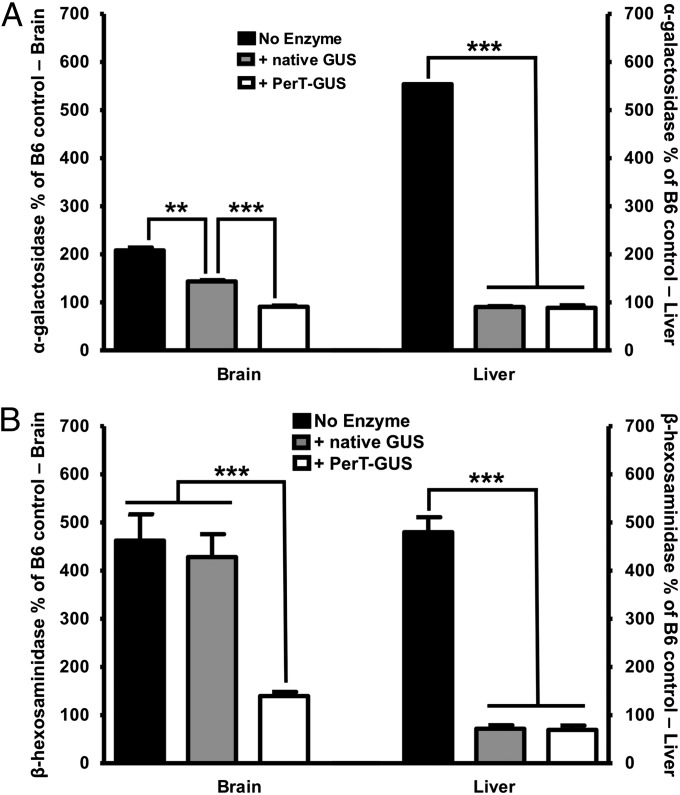
Fig. 4.
(A) α-Galactosidase levels after 12 weekly injections with either native or modified GUS. Both enzymes significantly decreased α-galactosidase levels in the brain (P = 0.0003 for native GUS and P < 0.0001 for PerT-GUS). However, PerT-GUS restored α-galactosidase levels to those of wild-type control mice. In the liver, both treatments produced a complete correction of secondary elevations and no significant difference between native GUS and PerT-GUS was observed. Enzyme activities are expressed as percentage of wild-type controls. Wild-type control mice have α-galactosidase-specific activities of 12.2 μ/mg in the brain and 24.9 μ/mg in the liver (n > 8). (B) Reduction in secondary elevation of β-hexosaminidase after 12 weekly infusions. In brain, only PerT-GUS showed efficacy in reducing β-hexosaminidase activity (P = 0.0008). In liver, both enzymes were equally effective and produced complete correction of secondary elevation of β-hexosaminidase. Enzyme activities are expressed as percentage of wild-type controls. Wild-type control mice have β-hexosaminidase-specific activities of 2,551 μ/mg in the brain and 1,773 μ/mg in the liver (n > 8).