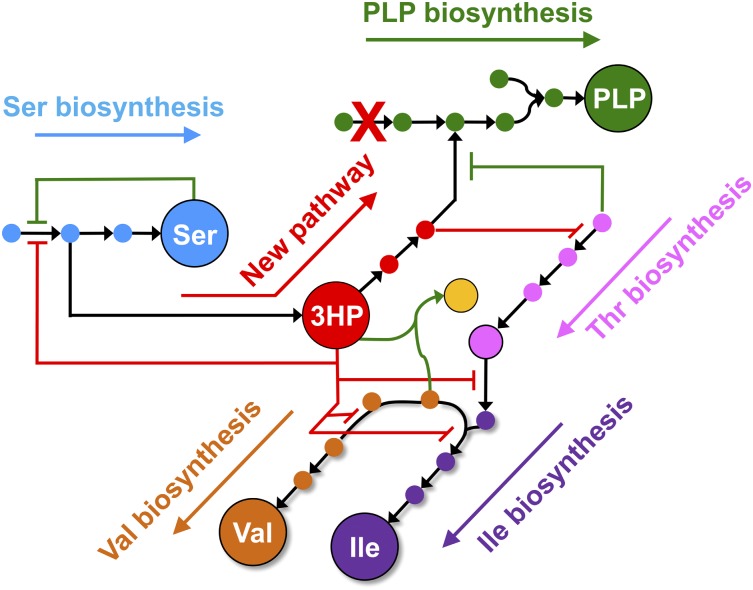
Fig. P1.
Summary of interactions between the normal metabolic network of E. coli and a novel pathway for the synthesis of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP). The E. coli strain lacks the gene required for PLP synthesis that is marked by X. Under these circumstances, PLP synthesis can be restored by overproduction of either YeaB or homoserine kinase. YeaB catalyzes the first step of the novel pathway; increasing levels of YeaB results in increased flux into the pathway. Homoserine kinase catalyzes the last step of the novel pathway; increasing levels of ThrB pulls material through the pathway (1). Red lines indicate inhibition of normal metabolic processes by metabolites in the novel pathway. Green lines indicate interference with the novel pathway by processes in the normal metabolic network.