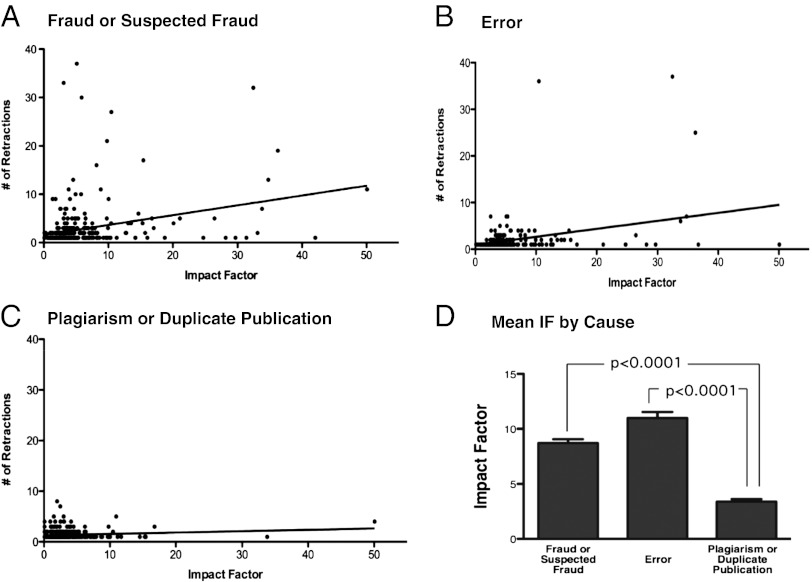
Fig. 3.
Relation of journal-impact factor to retractions for fraud or suspected fraud, error, and plagiarism, or duplicate publication. Journal-impact factor showed a highly significant correlation with the number of retractions for fraud or suspected fraud (A) (n = 889 articles in 324 journals, R2 = 0.08664, P < 0.0001) and error (B) (n = 437 articles in 218 journals, R2 = 0.1142, P < 0.0001), and a slight correlation with the number of retractions for plagiarism or duplicate publication (C) (n = 490 articles in 357 journals, R2 = 0.01420, P = 0.0243). The mean journal-impact factor of articles retracted because of fraud/suspected fraud or error was significantly different from that of papers retracted because of plagiarism or duplicate publication (D) (error bars ± SEM, P < 0.0001).