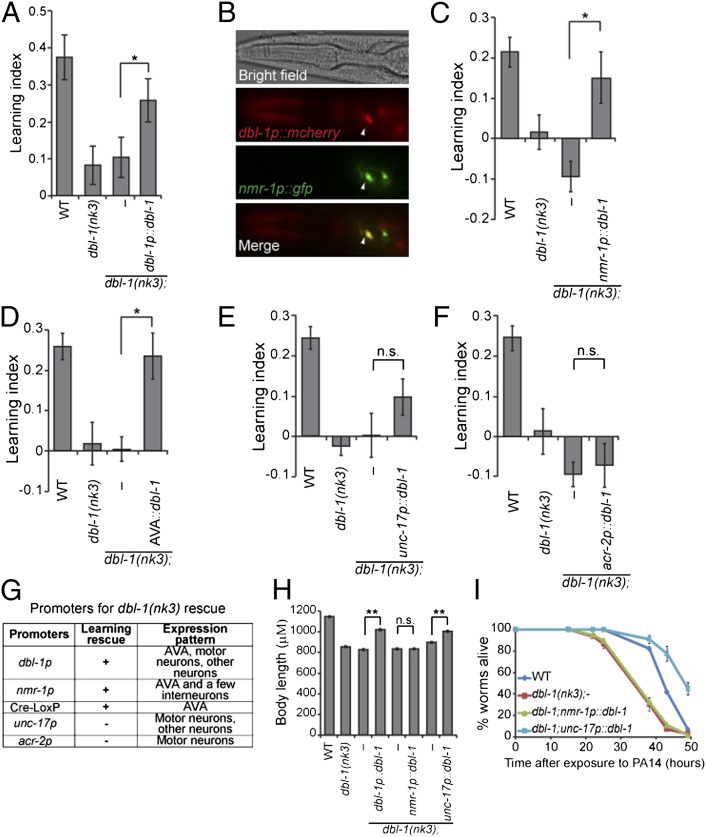
Fig. 2.
DBL-1 produced by the AVA interneurons mediates aversive olfactory learning. (A) dbl-1 genomic DNA rescues the learning defect of dbl-1(nk3) animals (n = 11 assays). (B) dbl-1 is expressed in the AVA (arrowheads). (C–F) Expression of dbl-1 using the nmr-1 promoter (C, n = 6 assays) or the AVA-selective expression of dbl-1 (D, n = 11 assays) rescues the learning defect of dbl-1(nk3) animals, but expression of dbl-1 using the unc-17 promoter (E, n = 13 assays) or the acr-2 promoter (F, n = 6 assays) does not rescue. (G) Promoters used in the dbl-1 rescue experiments. (H) Body length measurement (n ≥ 26 animals for each genotype). In A, C–F, and H, transgenic animals were compared with nontransgenic siblings using the paired Student t test (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05; n.s., P > 0.05; error bars represent SEM). (I) Representative individual slow-killing assays with the pathogenic bacterium PA14 (n ≥ 3 assays for each genotype, n ≥ 3 replicates in each assay; error bars represent SEM; Kaplan-Meier procedure and log–rank test; Table S1).