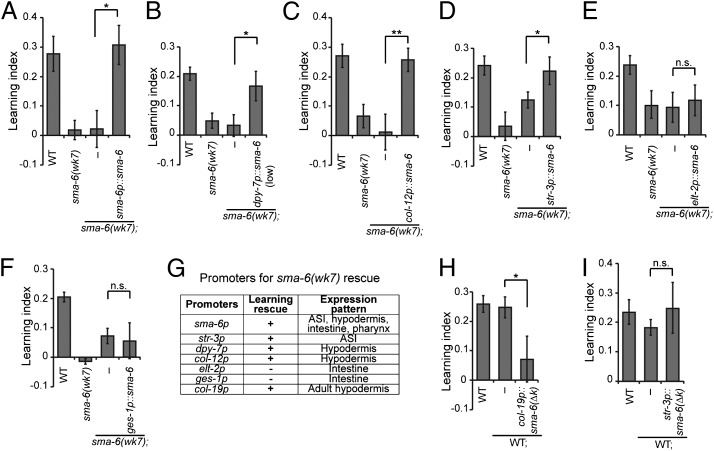
Fig. 3.
SMA-6 receptor acts in the hypodermis to facilitate aversive olfactory learning. (A) Genomic DNA of sma-6 rescues the learning defect of sma-6(wk7) mutant animals. (B–F) Expression of wild-type sma-6 in the hypodermis (B and C) or in the ASI neurons (D) rescues the learning defect of sma-6(wk7) animals, but expression of wild-type sma-6 in the intestine (E and F) does not rescue. (G) Promoters used in sma-6 rescue experiments. (H and I) Blocking DBL-1/SMA-6 signaling by expressing the dominant-negative sma-6(∆k) in the hypodermis (H) of wild-type animals impairs learning, but blocking DBL-1/SMA-6 signaling in ASI (I) has no effect. In A–F, H, and I, transgenic animals and nontransgenic siblings were compared using the paired Student t test (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05; n.s., P > 0.05; n ≥ 5 assays; error bars represent SEM).