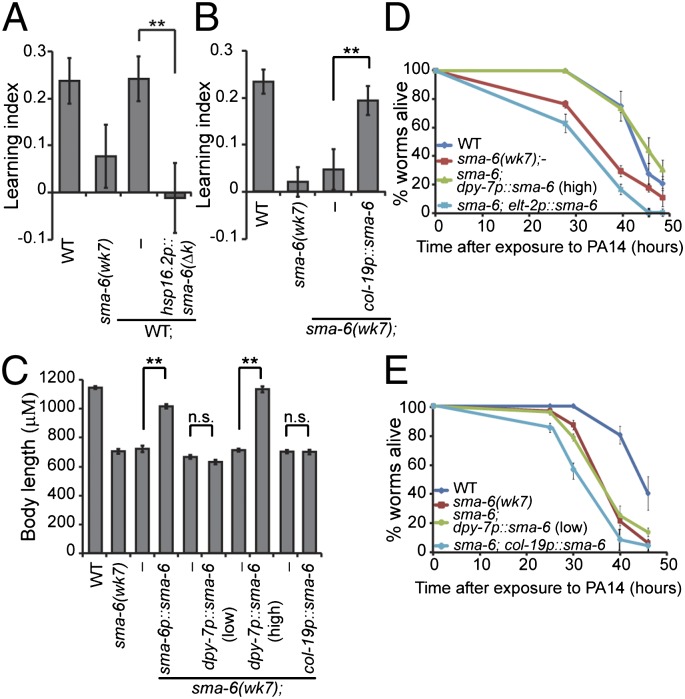
Fig. 4.
DBL-1/SMA-6 pathway acts during adulthood for aversive olfactory learning. (A) Blocking DBL-1/SMA-6 signaling at a late developmental stage abolishes the learning ability of wild-type animals (n = 6 assays). (B) Adult-specific expression of wild-type sma-6 activity in the hypodermis rescues the learning defect of sma-6(wk7) animals (n = 13 assays). (C) Body length measurements (n ≥ 23 animals each genotype). In A–C, transgenic animals were compared with nontransgenic siblings using the paired Student t test (**P < 0.01; n.s., P > 0.05; error bars represent SEM). (D and E) Representative individual slow-killing assays with the pathogenic bacterium PA14 (n ≥ 3 assays for each genotype, n ≥ 3 replicates in each assay; error bars represent SEM; Kaplan-Meier procedure and log–rank test; Table S1).